Warfarin
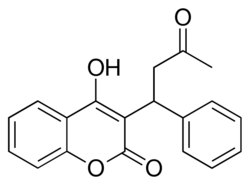 Chemical structure of warfarin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(RS)-4-Hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)- 2H-chromen-2-one
| |
| Other names
4-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-butyl)-2H-chromene
4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one Coumadin Coumafene Prothromadin | |
| Properties | |
| C19H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 308.333 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.4 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 161 °C (322 °F; 434 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 0.17 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, chloroform, DCM, dioxane Moderately soluble in ethanol, isopropanol, methanol, some oils Freely soluble in alkaline aqueous solution (forms a water-sol sodium salt) Practically insoluble in benzene, cyclohexane, hexane, pentane |
| Solubility in acetone | 6.5 g/100 ml (20 °C) |
| Solubility in chloroform | 5 g/100 ml (20 °C) |
| Solubility in dioxane | 10 g/100 ml (20 °C) |
| Vapor pressure | 0.09 mmHg at 20 °C |
| Acidity (pKa) | 5.87 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | DuPont |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
1.6 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is an organic chemical compound, used and sold as anticoagulant (blood thinner) in medicine and as rat poison.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Warfarin consists of a racemic mixture of two active enantiomers—R- and S- forms—each of which is cleared by different pathways. S-warfarin is 2-5 times more potent than the R-isomer in producing an anticoagulant response.
Physical
Warfarin is a colorless solid, odorless and tasteless. It is almost insoluble in water, but more soluble in some organic solvents, like acetone, halogenated solvents (chloroform e.g.), dioxane and somewhat soluble in alcohols.
Availability
Warfarin is sold in pharmacies, though it can only be acquired via prescription.
It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
Preparation
Warfarin can be prepared from coumarin, which itself can be obtained from the fermentation of sweet clover, though the amount obtained from this route is very small to be practical. It's better to use synthetic coumarin as precursor.
A much quicker route involves 4-hydroxycoumarin and benzalacetone. The reaction produces racemic warfarin.
Projects
- Pesticide
- Compound collecting
Handling
Safety
Warfarin is toxic if ingested and large amounts may lead to death. Vitamin K is used as antidote.
Storage
Warfarin should kept in sealed vials, with a proper hazardous chemical label, in a locked cabinet.
Disposal
Should be destroyed with an oxidizing mixture, like chromic acid, Fenton's reagent or piranha solution.