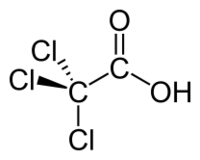
Trichloroacetic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Trichloroethanoic acid
| |
| Other names
TCA
Trichloracetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2HCl3O2 CCl3COOH | |
| Molar mass | 163.38 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.63 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 57.5 °C (135.5 °F; 330.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 195.5 °C (383.9 °F; 468.6 K) |
| 8.17 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | Miscible with acetone, alcohols, benzene, diethyl ether, methanol Slightly soluble in carbon tetrachloride |
| Solubility in acetone | 850 g/100 g (25 °C) |
| Solubility in benzene | 201 g/100 g (25 °C) |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | 617 g/100 g (25 °C) |
| Solubility in methanol | 2143 g/100 g (25 °C) |
| Solubility in xylene | 110 g/100 g (25 °C) |
| Vapor pressure | 1 mmHg (51.1 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.66 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
3.320 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Acetic acid Chloroacetic acid Dichloroacetic acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Trichloroacetic acid or TCA is an organic chemical compound, an analogue of acetic acid in which the three hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have all been replaced by chlorine atoms. It has the chemical formula CCl3COOH.
Contents
[hide]Properties
Chemical
TCA is a strong acid, which reacts with bases in solution to give salts.
It can decarboxylate in solution to form chloroform, especially as a salt.[1][2][3]
Physical
Trichloroacetic acid is a colorless crystalline hygroscopic solid, soluble in water and organic solvents.
Availability
Trichloroacetic acid is sold by chemical suppliers. Sometimes it is sold by some dentistry suppliers, usually as a solution.
Preparation
TCA can be synthesized by complete chlorination of acetic acid, with acetic anhydride as a catalyst, in the presence of UV light. Some sources indicate that sulfur[4] or red phosphorus[5] can also be used as catalysts.
- CH3COOH + 3 Cl2 → CCl3COOH + 3 HCl
This reaction also produces acetyl chloride and chloroacetyl chloride as side products, which may be recovered via fractional distillation if desired.
Projects
- Precipitation of macromolecules in biochemistry (proteins, DNA, RNA)
- Make dichloroacetic acid
- Make trifluoroacetic acid
Handling
Safety
Trichloroacetic acid is corrosive and harmful. Should be handled with proper protection.
Storage
Trichloroacetic acid should be kept in closed air-tight bottles, preferably in a desiccator.
Disposal
Adding an excess base will neutralize the compound. The compound can also be reduced to acetic acid using metallic powders.
Lastly, it can also be strongly diluted in water before being poured down the drain.
References
- Jump up ↑ Chemplayer, Chloroform from trichloroacetic acid, https://www.bitchute.com/video/p1ywta1RsCJN/
- Jump up ↑ F. H. Verhoek, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 3, 571–577, doi.org/10.1021/ja01318a014
- Jump up ↑ G. A. Hall Jr., F. H. Verhoek, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 3, 613–616, doi.org/10.1021/ja01195a044
- Jump up ↑ http://www.prepchem.com/synthesis-of-chloroacetic-acid/
- Jump up ↑ https://www.erowid.org/archive/rhodium/chemistry/chloroacetic.html
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
- Chemical pages without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Organic compounds
- Organochlorine compounds
- Acids
- Strong acids
- Carboxylic acids
- Solids
- Irritants