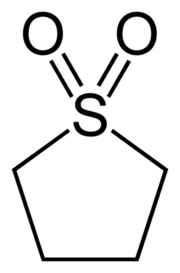
Sulfolane
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1λ6-Thiolane-1,1-dione
| |
| Other names
Tetrahydrothiophene 1,1-dioxide
Tetramethylene sulfone | |
| Properties | |
| C4H8O2S | |
| Molar mass | 120.17 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless solid |
| Odor | Odorless (pure) |
| Density | 1.261 g/cm3 (25 °C) |
| Melting point | 27.5 °C (81.5 °F; 300.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Solubility | Miscible with acetone, benzene, ethanol, toluene |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0062 mmHg at 27.6 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 165 °C (329 °F; 438 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
1,900 mg/kg (mouse, oral) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sulfolane or tetramethylene sulfone, is an organosulfur compound, formally a cyclic sulfone, with the formula (CH2)4SO2.
Contents
[hide]Properties
Chemical
Sulfolane resists oxidation by many oxidizing agents.
Physical
Sulfolane is a colorless solid at standard conditions, miscible with water.
Sulfolane is one of the most efficient industrial solvents for separating aromatics from hydrocarbon mixtures.
Availability
Sulfolane is sold by chemical suppliers.
Preparation
Sulfolane is prepared by reacting butadiene with sulfur dioxide via a cheletropic reaction to give sulfolene, which is hydrogenated using Raney nickel as a catalyst to give sulfolane. Purification is done via separation and vacuum distillation.
Oxidizing tetrahydrothiophene with hydrogen peroxide at high temperatures yields sulfolane.
Projects
- Extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from hydrocarbon mixtures
- Vapor suppressant for hydrofluoric acid
Handling
Safety
Sulfolane has low toxicity and it's difficult to ignite.
Storage
In closed bottles.
Disposal
Should be burned in a special incinerator, with SOx scrubbers.