Propionic anhydride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Propanoic anhydride
| |
| Other names
Propanoic acid, anhydride
Propanoyl propanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
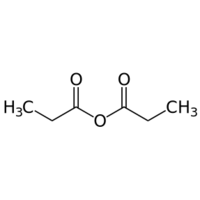
| C6H10O3 (CH3CH2CO)2O | |
| Molar mass | 130.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Pungent, rancid odor |
| Density | 1.015 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −42 °C (−44 °F; 231 K) |
| Boiling point | 167–170 °C (333–338 °F; 440–443 K) |
| Slowly hydrolyzes | |
| Solubility | Miscible with chloroform, diethyl ether, ethanol, isopropanol, methanol Slightly soluble in CCl4 |
| Vapor pressure | 1.36 mm Hg at 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 63 °C (145 °F; 336 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
2,360 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Acetic anhydride |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Propanoic anhydride or propionic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula (CH3CH2CO)2O.
Contents
[hide]Properties
Chemical
Propanoic anhydride slowly hydrolyzes in water to propionic acid.
Physical
Propionic anhydride is a colorless liquid, with a strong pungent smell, which is insoluble in water, but slowly hydrolyzes upon contact. It is miscible with most organic solvents.
Availability
Propionic anhydride is sold by chemical suppliers.
In the US, is it classified as a List I compound, due to its use in the illicit manufacturing of fentanyl and its analogues. As such it cannot be acquired by private individuals, and a license is required to purchase and use the compound.
Preparation
Propionic anhydride can be easily prepared by dry distilling a mixture of dry calcium propionate and propionyl chloride.
Alternatively, distilling a mixture propionic acid and oxalyl chloride will produce propionic anhydride, with a yield of 51%.[1]
Propanoic anhydride can also be obtained by dehydration of dry propionic acid using ethenone.
- 2 CH3CH2CO2H + CH2=C=O → (CH3CH2CO)2O + CH3CO2H
Another route is the Reppe carbonylation of ethylene with propionic acid and nickel carbonyl as the catalyst:[2]
- CH2=CH2 + CH3CH2CO2H + CO → (CH3CH2CO)2O
Projects
- Make esters
Handling
Safety
Propanoic anhydride is strong smelling and corrosive and will cause burns on contact with skin. Vapors can burn the eyes and lungs.
Storage
In closed bottles, away from moisture.
Disposal
Can be neutralized by adding it in a diluted NaOH or KOH solution, which causes it to hydrolyze to propionic acid and finally sodium or potassium propionate, respectively, which is harmless and can be poured down the drain or dumped in soil.
References
- Jump up ↑ https://www.prepchem.com/synthesis-of-propionic-anhydride
- Jump up ↑ https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14356007.a22_223.pub4
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
- Chemical pages without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Organic compounds
- Carboxylic acid anhydrides
- Foul smelling compounds
- Materials that react with water
- Materials unstable in basic solution
- DEA List I chemicals
- Liquids
- Irritants