Octyl acetate
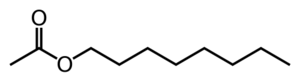
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Octyl acetate
| |
| Other names
Caprylyl acetate
Octyl ethanoate n-Octyl acetate | |
| Properties | |
| C10H20O2 | |
| Molar mass | 172.27 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fruity, slightly waxy floral odor |
| Density | 0.863–0.87 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −38.5 °C (−37.3 °F; 234.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 211 °C (412 °F; 484 K) |
| 0.021 g/100 g (0 °C) 0.018 g/100 g (29.7 °C) 0.018 g/100 g (40 °C) 0.012 g/100 g (92.1 °C) | |
| Solubility | Miscible with diethyl ether, ethanol, ethyl acetate |
| Vapor pressure | 0.01 kPa (−3 °C) 0.0072–0.0073 (14.75 °C) 0.02–0.1 kPa (27 °C) 1 kPa (66.3 °C) 10 kPa (120 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
3,000 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Ethyl acetate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Octyl acetate is an ester which is commonly found in citrus fruits.
Contents
[hide]Properties
Chemical
Octyl acetate can hydrolyze to 1-octanol and acetic acid. It can also act as a solvent.
Physical
Octyl acetate is insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol, 1-octanol and diethyl ether. It has a fruity smell. Octyl acetate has a wide liquid range. It melts at -38 °C and boils at 211 °C.
Availability
Octyl acetate may be extracted from oranges or grapefruits.
Preparation
As octyl acetate is an ester of 1-octanol and acetic acid, it can be synthesized by adding the two together in dehydrating conditions, though this is difficult.
Projects
- Extract octyl acetate from oranges or grapefruits
- Fragrant compound collecting
Handling
Safety
Octyl acetate is not particularly toxic, but do not ingest lab-grade material.
Storage
Should be stored in glass closed bottles, away from any flame source.
Disposal
Octyl acetate should be mixed with a more flammable solvent and safely burned.