4-Aminoantipyrine
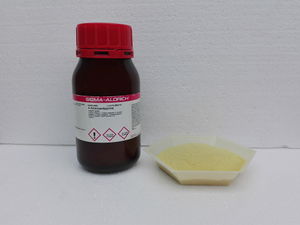 Old ampyrone and original bottle
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
4-Amino-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenylpyrazol-3-one
4-Amino-2,3-dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one | |
| Other names
4-Aminoantipyrene
Aminoantipyrine Aminoazophene Ampyrone Metapirazone Metapyrazone Solvapyrin A | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H13N3O | |
| Molar mass | 203.245 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.207 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 105–110 °C (221–230 °F; 378–383 K) |
| Boiling point | 309 °C (588 °F; 582 K) (decomposes) |
| 5.6 g/100 ml | |
| Vapor pressure | ~0 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 140.7 °C (285.3 °F; 413.8 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
1,700 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
4-Aminoantipyrine or ampyrone is an organic compound with the chemical formula C11H13N3O, used as reagent in analytical chemistry. It is the main metabolite of the anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drug Aminopyrine.
Contents
[hide]Properties
Chemical
4-Aminoantipyrine will decompose when heated to high temperatures.
Physical
4-Aminoantipyrine is a yellow odorless solid, soluble in water. Old samples tend to be have a more dark yellow to orange hue, due to degradation.
Availability
Ampyrone is sold by chemical suppliers.
Preparation
4-Aminoantipyrine is cheaper to buy than synthesize.
Projects
- Make various transition metal and lanthanide ligands
- Colorimetric determination of phenols
- Reagent for determination of glucose in the presence of phenol and peroxidase
Handling
Safety
4-Aminoantipyrine is irritant. It is the main metabolite of the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic drug Aminopyrine. Due to the risk of agranulocytosis its use as a drug is discouraged.[1]
Storage
4-Aminoantipyrine should be kept in air-tight closed amber bottles, away from light.
Disposal
4-Aminoantipyrine should be strongly diluted with lots of water before poured down the drain.
For complete neutralization, this compound should be carefully neutralized using an oxidizing mixture like chromic acid or Fenton's reagent, by adding it in small amounts. It can also be taken to waste disposal centers.
References
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
- Chemical pages without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Organic compounds
- Aromatic compounds
- Pyrazoles
- Amines