Difference between revisions of "Styphnic acid"
(Created page with "{{Chembox | Name = Styphnic acid | Reference = | IUPACName = 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzene-1,3-diol | PIN = | SystematicName = | OtherNames = 2,4-Dihydroxy-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene<br>2,...") |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| ImageAlt = | | ImageAlt = | ||
| ImageName = | | ImageName = | ||
| − | | ImageFile1 = | + | | ImageFile1 = Styphnic acid structure.png |
| − | | ImageSize1 = | + | | ImageSize1 = 180 |
| ImageAlt1 = | | ImageAlt1 = | ||
| ImageName1 = | | ImageName1 = | ||
Revision as of 21:01, 15 September 2022
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trinitrobenzene-1,3-diol
| |
| Other names
2,4-Dihydroxy-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene
2,4,6-Trinitro-1,3-benzenediol 2,4,6-Trinitroresorcinol | |
| Properties | |
| C6H3N3O8 | |
| Molar mass | 245.11 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.829 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 0.54 g/100 ml (25 °C) 1.15 g/100 ml (62 °C) 3.326 g/100 ml (96 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | Reacts with bases Soluble in nitric acid[2] |
| Solubility in 1,2-Diacetoxy ethane | 13 g/100 ml (20 °C)[3] |
| Solubility in acetone | 31.3 g/100 ml (17 °C) |
| Solubility in benzene | 47 g/100 ml (68 °C) 86 g/100 ml (80 °C)[4] |
| Solubility in carbon tetrachloride | 0.5 g/100 ml[5] |
| Solubility in ethanol | 5.1 g/100 ml (0 °C) 6.22 g/100 ml (17 °C) 14.65 g/100 ml (68 °C)[6] |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-467.5 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | None |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Picric acid Lead styphnate Trinitrophloroglucinol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
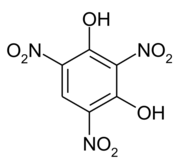
Styphnic acid or 2,4,6-trinitro-1,3-benzenediol (C6H3N3O8), is a yellow astringent acid (from Greek stryphnos "astringent") that forms hexagonal crystals.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Like picric acid, it is a moderately strong acid, capable of displacing carbon dioxide from solutions of sodium carbonate, for example.
It can also react with weakly basic oxides, such as those of lead and silver, to form the corresponding salts.
Physical
Trinitroresorcinol is a yellowish, crystalline solid, insoluble in water but more soluble in organic solvents.
Explosive
Styphnic acid is itself a low sensitivity explosive, similar to picric acid, but explodes upon rapid heating.
Availability
Styphnic acid is not sold by suppliers and has to be made.
Preparation
It may be prepared by the nitration of resorcinol with a mixture of conc. nitric and sulfuric acid.[7]
Projects
- Make lead styphnate
- Yellow dye
Handling
Safety
Styphnic acid is explosive and may explode if ignited. Like all nitroaromatics, it is toxic and will absorb through skin, staining it yellow.
Storage
Do not store it for long.
Disposal
Unlike other aromatic energetic compounds, styphnic acid cannot be safely burned as it may explode.
To safely neutralize it, it must first be diluted then chemically neutralized to less harmful products. One patent indicates that bubbling chlorine in an acidified dil. solution containing styphnic acid will destroy the compound.[8]
References
- ↑ Yalkowsky S.H., Yan H. Handbook of aqueous solubility data. - CRC Press, 2003
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-1-4899-0330-3_28
- ↑ Taylor; Rinkenbach; Journal of the American Chemical Society; vol. 48; (1926); p. 1309
- ↑ Орлова Е.Ю. Химия и технология бризантных взрывчатых веществ. - М., 1960 pp. 205
- ↑ Srinivasan; Mitra; Science and Culture; vol. 12; (1947); p. 502
- ↑ Орлова Е.Ю. Химия и технология бризантных взрывчатых веществ. - М., 1960 pp. 205
- ↑ http://www.powerlabs.org/chemlabs/styphnic.htm
- ↑ http://www.freepatentsonline.com/2487627.html