| Pages:
1
2 |
wg48
National Hazard
   
Posts: 821
Registered: 21-11-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Mabus  | As the guy who wrote the Mumetal page on the wiki, I feel the need to clarify than all the specs I've encountered about hard drives, say that the
magnet brackets are Mumetal,
snip |
Correct or not thanks for your work on the wiki Mabus.
Do you have a link to or a copy of one of those spec?
I have several magnets I extracted from defunct hard drives but I did not save the brackets. If you still have a bracket you could try cutting or
breaking one up to expose the core material and then attempt to dissolve it in HCl. I assume soft iron will dissolve easily.
I tried googling for material info on those brackets but did not find any primary reference. One utuber after noticing his screwdriver was more
strongly attracted to the magnet face than the opposite side on the bracket concluded the bracket was a magnetic shield and therefore was Mu metal an
erroneous conclusion. Any steel, soft iron or sufficiently magnetic material would have the same effect. Closing the loop round the magnets not only
increases their strength it also reduces stray fields. Mu metal shields would be placed as an outer shield specifically not in direct connection or in
the main flux path of the magnets to avoid magnetic saturation of the mu metal which would reduce its screening.
Of cause this does not preclude the material of the bracket being some other magnetic alloy compatable with the flux level of the neo magnets though I
doubt that they are.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Mabus  | As the guy who wrote the Mumetal page on the wiki, I feel the need to clarify than all the specs I've encountered about hard drives, say that the
magnet brackets are Mumetal, and that mumetal is specified to be a nickel alloy. I too have several magnet brackets from various different types of
hard drives, but unlike some people here, I haven't had any success dissolving anything: HCl gave me no reaction, adding a bit of 3% hydrogen peroxide
gave me just a little rust, which, given that the alloy has iron, it should be expected, but other than than slight coloring of the solution, not much
has happened. Sulfuric acid 30% didn't do anything. The only more corrosive stuff that I haven't tried are halogens, such as iodine or chlorine (as
bleach).
There is another possibility as to why you didn't get the nickel coloring: your "Mu-metal" from the brackets is not true mu-metal. Years ago, when I
took apart lots of hard drives, I found an old hard drive that had galvanized brackets and what I think it was a samarium-based magnet (well, some old
but strong magnets). I found it odd why it won't be nickle plated like the rest of the hard drive magnet brackets, so I added a bit of acid, but not
much happened. The next day the bracket was covered in rust in the area where I added the acid, which led me to believe that it probably wasn't a
nickel alloy, but rather some iron alloy with high magnetic permeability, probably because it was cheaper, or because nickel alloys were more
expensive back then.
Another possibility is that it is a nickel alloy, but for some reason only the iron dissolves. It's not the first time I've encountered nickel alloys
that "rust". A few years ago I scavenged some heating elements that were very rusty, but when I placed them in HCl acid, the only thing that happened
is that the rust was removed, while the metal wire did not dissolve, even after a few days of sitting in acid. Well, I assume the wire was nickel
alloy, since if it was chromium alloy, some of it should have dissolved. |
I believe the reason that I have a reaction from HCl/H2O2 and you did not was because my bracket was scratched in several places, letting the acid get
to the iron inside.
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
battoussai114
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 235
Registered: 18-2-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: Not bad.... Not bad.
|
|
Have you, Vsper or Mabus, tried and oxidizing acid like nitric? might be worth a shot dissolving the possible mumetal coat.
Quote: Originally posted by fusso  | If Ni in mumetal didn't dissolve in acids then why Ni in stainless steel do dissolve?
I tried dissolving SS in HCl previously and all Ni dissolved. |
Generally Nickel and it's alloys don't handle HCl or chlorides particularly well. But alloys are complicated and maybe there's some intergranular
attack happening at an iron rich boundary of a nickel rich intermetallic that's resistant to the acid attack, I'd expect this to result in something
similar to the selective leaching we see in dezincification of brass.
(Just speculating here though)
Batoussai.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
Here is what the solution looks like now. The picture was taken during light heating.
The solution is now much more green rather yellow. This is probably ferrous chloride (+3). The skin of the bracket is slightly tarnished now.
I am hoping that the coating will not dissolve, allowing me to experiment with it.

Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
Everything has dissolved, coating and all. The solution looks like very strong ferric chloride.
Are there any tests I could use for determining chromium, nickel, or copper content. I have a visible light spec I could use so that could tell me a
lot. I could look for absorbance peeks for copper and nickel chloride. Are there any databases with that data?
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
Texium
Administrator
       
Posts: 4626
Registered: 11-1-2014
Location: Salt Lake City
Member Is Offline
Mood: PhD candidate!
|
|
Add concentrated ammonia to it until it is highly basic, then filter out any precipitate formed. Nickel and copper should be left in solution as their
amine complexes while iron precipitates. If the solution is blue/purple, that's already a good indicator of a significant amount of nickel being
present. You should be able to look up the maximum absorbance values for these coordination complexes, and therefore be able to use your spec and a
quick Beer's law calculation to determine the concentration.
|
|
|
walruslover69
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 235
Registered: 21-12-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Another potential method could be to use acetone. I found that both iron chlorides are very soluble in acetone. So i would recommend boiling down your
solution and precipitating your NiCl2 with acetone which is negligibly soluble.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
I can not find any data on the solubility of nickel chloride in acetone.
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
walruslover69
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 235
Registered: 21-12-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I could only find this one source
https://books.google.com/books?id=7L0MAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA537&...
I also found ferric chloride to be 10 times more soluble that nickel chloride in ethanol.
http://periodic-table-of-elements.org/SOLUBILITY/ferric-III_...
http://periodic-table-of-elements.org/SOLUBILITY/nickel-II_c...
Upon further look I believe those numbers are only for the anhydrous salts and so precipitating out might not work very well, but evaporating the
water and baking the salts to dehydrate them and then redissolving the iron in acetone or water would probably work.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
I have a liter of dry ethyl alcohol I received for free as a sample. I could use that after roasting the solution's solutes in a steel can (to prevent
breaking or damaging a beaker).
Ferric Chloride decomposes at 280C to the anhydrous salt and I will have to take care not to heat it above 316. This presents a difficulty as I have
no way to measure that temperature. Anhydrous nickel chloride does would be safe to roast on a hotplate without fear of decomposition.
What other sources of nickel metal are there? Any pure?
[Edited on 1-6-2018 by VSEPR_VOID]
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
walruslover69
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 235
Registered: 21-12-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I don't see a reason why you would want/need to oxidize to ferric chloride in the first place. Ferrous chloride has similar solubility in ethanol
(100g/100ml).
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/047084289X.ri055
Both nickel and ferrous chloride are heat stable up to like 500+ degrees so you shouldn't have a problem drying them that way. Alternatively you could
dry them through azeotropic distillation with toluene but that sounds like a lot of work.
I don't know of any OTC sources of pure nickel. If you live here in the U.S then 5 cent nickel coins could be a promising source. They are 25% nickel
and 75% copper. I would estimate that there would be minimum impurities, since the Mint keeps relatively high standards. I have actually been
considering doing this for a long time but I have been hesitant to waste some of my nitric acid on it.
|
|
|
wg48
National Hazard
   
Posts: 821
Registered: 21-11-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by VSEPR_VOID  |
I have a liter of dry ethyl alcohol I received for free as a sample. I could use that after roasting the solution's solutes in a steel can (to prevent
breaking or damaging a beaker).
|
Perhaps you will discover a way to get the nickel out if you put the solution in a steel can. I think iron will displace nickel from its chloride
solution and therefore will plate out on to the steel can. Ok that does not help separate the nickel from the iron in the can if its adherent but you
will know if nickel is in the solution. You will need the can surface to be clean and not tinned and/or not coated.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by wg48  | Quote: Originally posted by VSEPR_VOID  |
I have a liter of dry ethyl alcohol I received for free as a sample. I could use that after roasting the solution's solutes in a steel can (to prevent
breaking or damaging a beaker).
|
Perhaps you will discover a way to get the nickel out if you put the solution in a steel can. I think iron will displace nickel from its chloride
solution and therefore will plate out on to the steel can. Ok that does not help separate the nickel from the iron in the can if its adherent but you
will know if nickel is in the solution. You will need the can surface to be clean and not tinned and/or not coated. |
I think that would work as long as I can remove the zinc coating. Alternatively I could just find some iron nails or wool.
[Edited on 1-6-2018 by VSEPR_VOID]
[Edited on 1-6-2018 by VSEPR_VOID]
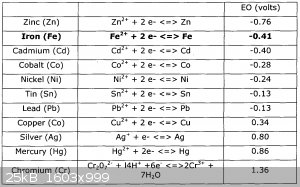
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
Update:
The brackets are just clearly an alloy of iron with a coating of nickel. The solution resulting from dissolving them in HCl-H2O2 is not worth
separating.
That being said I did go ahead and boil the solution as I said I would do in a steal can. The solution became bright green and the surface of the can
became eroded and and dull in color. The resulting solution was filtered and boil down by 30%. Upon cooling a film of white crystals formed. The green
is probably from ferrous chloride after the ferric chloride was reduced by the steel during boiling. Nickel metal must have precipitated out and been
replaced with iron/zinc in solution.
Nickel can be separated alternatively from US nickels so going out and finding hard drive brackets is not worth it.
Important Proceedings
After completely boiling down the solution I was left with fluffy green crystals pictured bellow. I proceeded to take a gram of this material and
place it in a test tube with water, then added strong sodium hydroxide solution and heated. The results of this are also pictured bellow. I expected
iron hydroxide then iron oxide to appear, but instead a blackish-blue precipitate appeared along side some red iron oxide. When ~32% hydrochloric acid
was added to this precipitate it dissolved to form a yellow solution free of undissolved material.
[Edited on 2-6-2018 by VSEPR_VOID]
 
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
wg48
National Hazard
   
Posts: 821
Registered: 21-11-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Some tape cassette player motors have what I believe is a mu-metal sleeve on them. see the pic below. I have not chemically confirmed that the sleeve
contains a significant percentage of nickel. Of cause these days it may be hard to find an old tape cassette player.
The grey material under the label is the mu-metal or some other high mu magnetic screening material

|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
I could swear I have seen metal ribbons around the casing like that on other motors. Is it specifically that one type of motor?

Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
wg48
National Hazard
   
Posts: 821
Registered: 21-11-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by VSEPR_VOID  | | I could swear I have seen metal ribbons around the casing like that on other motors. Is it specifically that one type of motor?
|
No its for any motor that may interfere with what ever the motor is in. I have also seen L shaped sheets above turntable motors and open-ended boxes
over mains transformers, which I assumed were mu metal.
One motor I have is like yours and it has a sleeve on it but I think it was from a vacuum cleaner. The shield is a dull grey colour similar to the mu
metal shields on oscilloscopes tubes. It is not like the silver shiny main body of the motor. But why use Mu metal for a vacuum cleaner motor?
So rather than mislead you I cut a small piece off the shield and a small piece of zinc plated steel. I put both in test tubes containing 28% HCl.
Both are vigorously bubbling. I conclude that both are mostly iron. So I now doubt if any of those small motors have Mu metal shields. I have a very
fancy tape drive for data storage but modern hard drives have made it redundant. Its got a nice case I could use so I will check its motors at some
point when it get dismantled.
I just checked the test tubes again both are in a water bath at about 60C. Both look very similar vigorously bubbling and the both solutions are a
light slight greenish yellow colour. If anything the soft iron is bubbling a little more.
|
|
|
NEMO-Chemistry
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1559
Registered: 29-5-2016
Location: UK
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I posted a while back about Nickel, i had flakes and wanted chloride. I thought i had failed because i got something the wrong way around!!
I used ferric chloride acidified with HCL (your supposed to also add a Amine for speed) I did post a reference somewhere for this i think its in refs,
and i am pretty sure its from the JCE.
It dissolves slowly without a AMINE, but when i added ammonia it formed a kind of 'gloop' i thought tjhis was iron from the ferric chloride at the
time and threw it away.
The solution looked very dark and some (a fair bit) of Nickel was left in the tube. I let mine react for 5 days!!! but i am told if you add the amine
and gently heat then its just a few hours.
When i added water i did get a greenish colour so maybe it did work!! I will try again tomorrow as i could really use some Nickel Chloride to do some
plating.
I did a quick search but cant find my post, i am also fairly sure its one the few experiments i took a few pics of, trust me dissolving Nickel is not
a spectator sport!
Sorry it was a web page i got it from, isnt the guy a member here?
http://lanthanumkchemistry.over-blog.com/article-the-dissolv...
and another
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2FBF00728908
[Edited on 2-6-2018 by NEMO-Chemistry]
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
I went looking and found a motor from I think a printer that had one of those metal sleeves on it. It was easy to remove with a knife. It is not
easily bent and is a dull grey. I will get some more H2O2 tomorrow and try to dissolve it.
There is a brand of pool hydrogen peroxide at my local publix that is 10% strength. I am considering trying to concentrate it.
I left out the yellow crystals in sunlight, in a clear jar with a desiccant, to dry and they turned yellow. I am sure this is the result of ferrous
chloride oxidizing somehow back to the ferric salt. This makes me rather sad as I enjoyed the original color.
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
wg48
National Hazard
   
Posts: 821
Registered: 21-11-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by VSEPR_VOID  | I went looking and found a motor from I think a printer that had one of those metal sleeves on it. It was easy to remove with a knife. It is not
easily bent and is a dull grey. I will get some more H2O2 tomorrow and try to dissolve it.
There is a brand of pool hydrogen peroxide at my local publix that is 10% strength. I am considering trying to concentrate it.
I left out the yellow crystals in sunlight, in a clear jar with a desiccant, to dry and they turned yellow. I am sure this is the result of ferrous
chloride oxidizing somehow back to the ferric salt. This makes me rather sad as I enjoyed the original color. |
Cut a small peice off and see if it desolves in plain HCl before you start with H2O2/HCl to check if its soft iron.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by wg48  | Quote: Originally posted by VSEPR_VOID  | I went looking and found a motor from I think a printer that had one of those metal sleeves on it. It was easy to remove with a knife. It is not
easily bent and is a dull grey. I will get some more H2O2 tomorrow and try to dissolve it.
There is a brand of pool hydrogen peroxide at my local publix that is 10% strength. I am considering trying to concentrate it.
I left out the yellow crystals in sunlight, in a clear jar with a desiccant, to dry and they turned yellow. I am sure this is the result of ferrous
chloride oxidizing somehow back to the ferric salt. This makes me rather sad as I enjoyed the original color. |
Cut a small peice off and see if it desolves in plain HCl before you start with H2O2/HCl to check if its soft iron. |
The metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid so it probably either iron or covered in zinc (which is my bet). Most electronic casings tend to be
plated in a thin layer of zinc metal to protect against corrosion.
Left most beaker: The original salt after drying. Notice it turned back to yellow-brown indicating the ferrous salt oxidized.
Middle beaker: The result of treating a solution of the salt with large amounts of concentrated ammonia. The precipitate was filtered, washed with
water, and is being dried.
Right test tube in beaker: Magnatite (Fe3O4) which was confirmed by placing a magnet near it. This was made by treated the salt with concentrated
sodium hydroxide.
Conclusion
The brackets in the hard drive are almost entirely iron with trace amounts of what is possibly nickel. This was an interesting exercise known the
less. I recommend that the SM wiki be changed to include this information. For future study I will continue to investigate the "mu-metal" cover of
motors.
 
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
Mabus
Wiki Master
  
Posts: 238
Registered: 3-11-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: Energetic
|
|
@VSEPR_VOID I have tried to find the information where I found the mention of Mu-metal being used in hard drive brackets, but so far haven't found
much.
I did find, however, this thread on the Goldrefiningforum, where a person tested some hard drive brackets with nitric acid, and compared the result with a few nickel
pennies. Apparently the silvery ones are nickel alloy. Somebody there also mentioned that Mumetal was also used in the outer frames of some old
computers and hard drives. I have encountered many old hard drives with some flat plates of various forms, but I've not collected them since some were
magnetic and others were not, so I just assumed they were some stainless steel (they also didn't rust easily).
Also, he sent one sample to analysis:
| Quote: |
ANALYSIS UPDATE:
On my huge heavy neo magnet holder plates. The ones I had were 10mm thick, and were curved like a C shape to accomodate the two large neos.
Confirmed that they are Mu-metal, and indeed have nickel in them, but mostly on a very thin surface layer.
I took the lot (about 30kg) to a local recycler to analyse with test gear.
They tested surface and found 85/15 nickel/iron %, and cut in half, tested center to find 2/98 nickel/iron %, and the same with a micron abraded
surface.
So there you go, mostly iron with 2% nickel, and a fine surface layer of nickel, probably there to simply protect the iron from rusting.
These figures are from *MY* Mu-metal pieces, and are quoted from memory, I have exact written down somewhere and will edit when and if I can.
I got about NZ$16 for the iron content, with the nickel classed as a contaminant!
SK |
That's not a lot of nickel, not sure if it was because those brackets were huge. I'd really like to see what would be the percentage of nickel for
laptop hard drive brackets, since those are very thin, where it'd be simpler for them to be Mumetal than a thin sheet of iron with Mumetal plating.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
That sounds about right and my results support his findings. Mostly iron. I hope the motor metal coverings prove to be more interesting.
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
Bezaleel
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 444
Registered: 28-2-2009
Member Is Offline
Mood: transitional
|
|
Maybe slightly of-topic, but when you're after nickel, why don't you try a pottery supplies shop and look for black nickel oxide. This oxide has the
approximate formula Ni2O3. It is a cancerous substance, so take care when handling it.
Black nickel oxide dissolves only in strong HCl solution on heating. No reaction with H2SO4 whatsoever, or with oxidising acids, like HNO3.
|
|
|
VSEPR_VOID
National Hazard
   
Posts: 719
Registered: 1-9-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: Fullerenes
|
|
I would prefer not to buy it. It seems a bit like cheating.
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
Within cells interlinked
|
|
|
| Pages:
1
2 |