| Pages:
1
2 |
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Protecting groups for tertiary amines
Greetings!
I was wondering if any of you have some input about a problem for a synthesis I'm facing atm.
Basically, I want to use this compound (Figure 1)
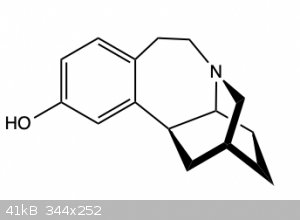
to make this compound (Figure 2)
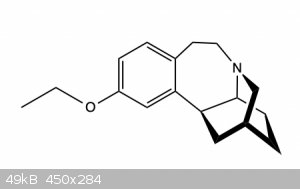
Basically this is just an ether synthesis, but the problem is that the molecule also contains a tertiary amine and so should be protected to avoid
over alkylation to a quaternary ammonium ion.
I have been looking at Wuts "Protective groups for organic synthesis" extensively, but the problem is that the protective groups shown there are all
basically derivatives of acetic anhydride, which is a schedule 1 precursor (I think cartels use it to acetylate morphine or something...). In any
case, this would mean that the standard protecting groups are off the table for me unfortunately (not judging what others choose to do, just saying).
I have noticed however, that when converting a quaternary ammonium ion to a tertiary amine, the alkyl substituent that is expelled is the most
substituted of the four. So maybe a strategy would be to first "over alkylate" the amine by adding a t-butyl group onto it, forming the ether, and
then removing the redundant "protective" alkane from the amine.
Unfortunately, I couldn't find any consistent sources on how to turn a quaternary ammonium ion into a tertiary amine.
If any of you know how to do this (or if the proposed method even has a chance of succeeding I would love to hear from you! If you know of other, less
restrictive protecting groups that might work here, the I'd be super curious to learn about those too!
Below is the proposed synthesis (Figure 3)
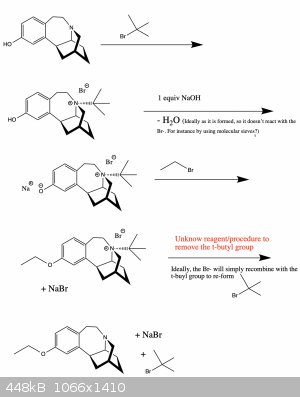
References:
Wuts, Peter GM, and Theodora W. Greene. Greene's protective groups in organic synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, 2006.
[Edited on 7-7-2021 by Monoamine]
|
|
|
karlos³
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1520
Registered: 10-1-2011
Location: yes!
Member Is Offline
Mood: oxazolidinic 8)
|
|
Boil it in ethanolamine to dequaternise.
|
|
|
zed
International Hazard
    
Posts: 2284
Registered: 6-9-2008
Location: Great State of Jefferson, City of Portland
Member Is Offline
Mood: Semi-repentant Sith Lord
|
|
Find a reference for the procedure.
Need for a protecting group is not certain.
Some alkylating agents might attack that tertiary amine, and some might not.
|
|
|
Jenks
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 163
Registered: 1-12-2019
Member Is Offline
|
|
A very similar structure is ibogaine. Here is a patent where its methyl ether is converted into an ethyl ether while the tertiary nitrogen is protected by temporarily converting it into a
lactam.
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Amazing! Thank you for all the helpful replies!
Time to hit the books 
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Jenks  | | A very similar structure is ibogaine. Here is a patent where its methyl ether is converted into an ethyl ether while the tertiary nitrogen is protected by temporarily converting it into a
lactam. |
Out of curiosity: Do you happen to know if the compounds in the patent you linked ever made it to pre-clinical trials and if their in vitro
pharmacology was ever studied? In particular, was their affinity for the human HERG channel ever investigated?
|
|
|
Dr.Bob
International Hazard
    
Posts: 2748
Registered: 26-1-2011
Location: USA - NC
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
You could also oxidize the tert amine to the N-oxide and that would stable and then reduce it back later.
|
|
|
Jenks
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 163
Registered: 1-12-2019
Member Is Offline
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Monoamine  | Quote: Originally posted by Jenks  | | A very similar structure is ibogaine. Here is a patent where its methyl ether is converted into an ethyl ether while the tertiary nitrogen is protected by temporarily converting it into a
lactam. |
Out of curiosity: Do you happen to know if the compounds in the patent you linked ever made it to pre-clinical trials and if their in vitro
pharmacology was ever studied? In particular, was their affinity for the human HERG channel ever investigated? |
The patent is from 1959 and I haven't found any other reference to O-ethyl-noribogaine, except as a way of derivitizing noribogaine for HPLC analysis.
But ibogaine and noribogaine have been extensively studied.
This seems like the easiest method if it works. If ethyl is too bulky, the amine could be methylated, then the phenol ethylated, then the amine
demethylated with ethanolamine or a thiolate. Still one pot.
[Edited on 7-7-2021 by Jenks]
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Jenks  | Quote: Originally posted by Monoamine  | Quote: Originally posted by Jenks  | | A very similar structure is ibogaine. Here is a patent where its methyl ether is converted into an ethyl ether while the tertiary nitrogen is protected by temporarily converting it into a
lactam. |
Out of curiosity: Do you happen to know if the compounds in the patent you linked ever made it to pre-clinical trials and if their in vitro
pharmacology was ever studied? In particular, was their affinity for the human HERG channel ever investigated? |
The patent is from 1959 and I haven't found any other reference to O-ethyl-noribogaine, except as a way of derivatizing noribogaine for HPLC analysis.
But ibogaine and noribogaine have been extensively studied.
This seems like the easiest method if it works. If ethyl is too bulky, the amine could be methylated, then the phenol ethylated, then the amine
demethylated with ethanolamine or a thiolate. Still one pot.
[Edited on 7-7-2021 by Jenks] |
Indeed, Ibogaloids are a fascinating class of compounds, and we're probably only scratching the surface of their potential. Still, it would be nice to
find a compound possessing all of Ibogaine's therapeutic effects, but without blocking the HERG channel, which can cause cardiac arrhythmias at
extremely high doses in some people.
Noribogaine - the major, active metabolite of Ibogaine - which contributes to the total effects significantly, has an even higher affinity for the
HERG channel unfortunately.
But... I'm confident that much progress will be made in that area in the years to come.
I'm curious to hear what your thoughts are?
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Another possible way to for protection:
Just saw this: (https://www.organic-chemistry.org/protectivegroups/amino/tol...).
It seems that under the above conditions even a tosyl group can be used for protection of amines.

Not though, that protecting tertiary amines creates ammonium cations.
Reference:
A facile and efficient indium-catalyzed sulfonylation of amines allows the synthesis of a wide range of sulfonamides in excellent yields. The method
showed a generality for substrates including less nucleophilic and sterically hindered anilines, and it is also applicable for preparing sulfonic
esters from sulfonyl chlorides and alcohols.
J. Yan, J. Li, D. Cheng, Synlett, 2007, 2442-2444.
|
|
|
SWIM
National Hazard
   
Posts: 970
Registered: 3-9-2017
Member Is Offline
|
|
Wouldn't the ethyl bromide have to attack the tertiary amine via an SN2 pathway because of the relatively mild conditions that would be used to form a
phenol ether?
And wouldn't this be impossible because of the rigidity of the structure?
Not sure about this, but it looks like that nitrogen would have trouble doing the 'umbrella blown inside out' thing that is required for an SN2.
Disclaimer:
If this opinion is gibberish, I blame the dexamethasone and lenalidomide.
It's a combo that kinda sneaks up on you.
|
|
|
Oxy
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 140
Registered: 1-12-2020
Member Is Offline
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by SWIM  | Wouldn't the ethyl bromide have to attack the tertiary amine via an SN2 pathway because of the relatively mild conditions that would be used to form a
phenol ether?
And wouldn't this be impossible because of the rigidity of the structure?
Not sure about this, but it looks like that nitrogen would have trouble doing the 'umbrella blown inside out' thing that is required for an SN2.
|
I think in this case it would be in an other way around. Nitrogen's lone pair of electrons (exposed a bit due to structure and very basic due to 3
alkyl substituents) will attack ethyl bromide as nucleophile and substitute bromine.
That means there is no need and place for any structural inversion here.
|
|
|
Jenks
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 163
Registered: 1-12-2019
Member Is Offline
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Monoamine  |
Indeed, Ibogaloids are a fascinating class of compounds, and we're probably only scratching the surface of their potential. Still, it would be nice to
find a compound possessing all of Ibogaine's therapeutic effects, but without blocking the HERG channel, which can cause cardiac arrhythmias at
extremely high doses in some people.
Noribogaine - the major, active metabolite of Ibogaine - which contributes to the total effects significantly, has an even higher affinity for the
HERG channel unfortunately.
But... I'm confident that much progress will be made in that area in the years to come.
I'm curious to hear what your thoughts are? |
I agree with you that the structure-activity relationships of structures like ibogaine are a wide open and potentially highly helpful area. The few analogs that have been promoted (noribogaine, 18-methoxycoronaridine (18-MC), anything else?) have not shown better properties for treating addiction than ibogaine, as far as I am aware. The
main "feature" of noribogaine is supposed to be that it doesn't produce visionary effects, so as not to frighten the decision makers that might approve its use. But
a lot of people who have been treated for addiction with ibogaine credit the visions they had for helping them understand the causes of their
addiction and live differently. Addiction is extremely complicated and animals aren't a very good screen. For example, voacangine (16-carbomethoxy-ibogaine) was able to prevent withdrawal in rats, but mainly causes gastrointestinal distress in humans, maybe due to
a difference in metabolism of this difficult-to-hydrolyze ester. That wasn't discovered by some clinical trial though - it was found by volunteers at
an unregulated addiction treatment provider, the voacangine being available because it is the main precursor to ibogaine. And that doesn't bode well
for 18-MC, having the same ester group, which still hasn't started clinical trials for treating addiction despite being developed as a candidate for
that purpose in 1996.
Everything about ibogaine is an uphill battle. Drug addicts have been the group for the media to hate for a century, to the point where there is even
an insurmountable stigma against helping them. Howard Lotsof, the one who discovered ibogaine's anti-addictive effects in 1962, once asked a representative at a pharmaceutical company why they
would not develop ibogaine as a medication. Their candid reply was that the stigma of even helping drug addicts would cause so much loss in sales of
their other product lines that it would not be profitable. This is why, to this day, almost all addiction treatment with ibogaine is provided by
self-selected, unregulated providers - many of them former addicts themselves - trying to fly below the radar in countries like Mexico. So as
interesting as the chemistry and pharmacology of ibogaine is, the main problem with developing it remains psychological, even spiritual, affecting the
attitude of people throughout the world.
As far as promising analogs, Tabernanthe iboga itself contains ibogaline, ibogamine and tabernanthine, in order of amount, in addition to ibogaine. These probably have properties similar to ibogaine, differing only in number and
position of aryl methoxy groups, and any one might have a better pharmacological profile (which, in my mind, mainly means less chance of causing
cardiac arrhythmia). Another place to start is derivatization of the ibogamine skeleton, as was done with 18-MC, an isomer of voacangine. Also, the
methyl group on ibogaine could be replaced with other alkyl groups as we discussed. Finally, it may be possible to find Friedel-Crafts conditions that
would selectively functionalize the benzene ring in ibogaine, based on a reverse Friedel-Crafts alkylation of voacamine into voacangine that was recently published. This paper also described the isolation of voacristine from Voacanga africana, which allows analogs similar to 18-MC, and its de-esterified derivatives, to be made. It is also possible to functionalize the carbon on ibogaine where voacangine has its ester group. There are also a few other ibogamine derivatives available
from Tabernaemontana species which could be derivatized. The difficulty here is that the species would have to be cultivated, requiring both a farmer
and a chemist.
[Edited on 12-7-2021 by Jenks]
|
|
|
Texium
|
Threads Merged
12-7-2021 at 05:40 |
Texium
Administrator
       
Posts: 4618
Registered: 11-1-2014
Location: Salt Lake City
Member Is Offline
Mood: PhD candidate!
|
|
Stop posting multiple threads on the
same subject.
|
|
|
Triflic Acid
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 486
Registered: 27-9-2020
Member Is Offline
Mood: Slowly Oxidizing into Oblivion
|
|
Maybe try using diethyl carbonate. It seems that carbonates are unable to form quaternary ammoniums. You could make diethyl carbonate by heating
diethyl oxalate up so it breaks down to diethyl carbonate and carbon monoxide. Or, if you want to buy it, U2U me. I know a member with a large stock
he can sell.
[Edit: He has dimethyl carbonate, not diethyl. My bad.]
[Edited on 12-7-2021 by Triflic Acid]
There wasn't a fire, we just had an uncontrolled rapid oxidation event at the power plant.
|
|
|
EverythingAl2O3
Hazard to Self
 
Posts: 51
Registered: 3-9-2019
Member Is Offline
|
|
Is there anything stopping you from doing an acid catalyzed ether synthesis? So you could use H2SO4 and ethanol to get your phenethoxy group and avoid
the overalkylation?
|
|
|
njl
National Hazard
   
Posts: 609
Registered: 26-11-2019
Location: under the sycamore tree
Member Is Offline
Mood: ambivalent
|
|
Or deprotonate and perform William ether synthesis
Reflux condenser?? I barely know her!
|
|
|
Triflic Acid
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 486
Registered: 27-9-2020
Member Is Offline
Mood: Slowly Oxidizing into Oblivion
|
|
But the Williamson ether needs an alkyl halide, which will destroy the amine. Assuming you don't add a protecting group like the OP said.
There wasn't a fire, we just had an uncontrolled rapid oxidation event at the power plant.
|
|
|
njl
National Hazard
   
Posts: 609
Registered: 26-11-2019
Location: under the sycamore tree
Member Is Offline
Mood: ambivalent
|
|
I think the phenolate will react much more quickly compared to the amine.
Reflux condenser?? I barely know her!
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Thank you for the tip! (So just to clarify, this is done to deprotect the amine later?)
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Ahhh... you mean because a deprotonated OH (ie O-) will be far more likely to react with with the Br-Alkyl, than the weaker (lewis?) base which is the
lone pair on the amine.
I will try this for sure, if it works it'll definitely make thinks a lot easier!
Thanks!
|
|
|
njl
National Hazard
   
Posts: 609
Registered: 26-11-2019
Location: under the sycamore tree
Member Is Offline
Mood: ambivalent
|
|
Not exactly to deprotect, this method just accepts the quaternization and deals with it after the reaction rather than preventing it in the first
place.
| Quote: |
Ahhh... you mean because a deprotonated OH (ie O-) will be far more likely to react with with the Br-Alkyl, than the weaker (lewis?) base which is the
lone pair on the amine.
|
Yes. Although the nitrogen lone pair will probably be more nucleophilic than other tertiary amines due to the molecules geometry.
Reflux condenser?? I barely know her!
|
|
|
clearly_not_atara
International Hazard
    
Posts: 2799
Registered: 3-11-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: Big
|
|
It depends on the solvent conditions. A phenolate is more reactive than an amine. But in a less polar solvent, the phenol will be neutral (protonated)
and the amine will react first.
So first you must ensure the phenol is deprotonated.
You can also use weaker alkylating agents like diethyl oxalate, which should only attack the phenol here.
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
This seems like a pretty straight forward way to make acetal protected amines
This may be a bit late, but it seems pretty useful, so I'll post this here anyay:
Attachment: Acetal_amine_protection_procedure_(Sharley_2017.pdf (1.5MB)
This file has been downloaded 283 times
Basically, the authors have a way to apply pretty much any acetal protecting group to (secondary or primary) amines. The cool thing about this seems
to be that they only use relatively common reagents for all this. (No need for acid-halides etc...)
The only drawback that I can see is that there doesn't seem to be a very cleary way to determine how much catalyst (acetic acid) has to be used. The
amount can range from 0.1 eqiv to 2.5 equiv!! Also the reaction takes about 20h.
But still, unless you have some acetic anhydride or SOCl2 lying around, this definitely seems like a decent alternative, considering how
general it is.
Sharley, Daniel D. Sanz, and Jonathan MJ Williams. "Acetic acid as a catalyst for the N-acylation of amines using esters as the acyl source." Chemical
Communications 53, no. 12 (2017): 2020-2023.
|
|
|
Monoamine
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 168
Registered: 25-5-2021
Location: Sweden(ish)
Member Is Offline
Mood: +7
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by clearly_not_atara  |
It depends on the solvent conditions. A phenolate is more reactive than an amine. But in a less polar solvent, the phenol will be neutral (protonated)
and the amine will react first.
So first you must ensure the phenol is deprotonated.
You can also use weaker alkylating agents like diethyl oxalate, which should only attack the phenol here. |
Thank you for the tip! Would the solvent also have to be protic or would e.g. DMSO work. (Or would the Br-Et react with the alpha carbon of the
thionyl of DMSO?
|
|
|
| Pages:
1
2 |