| Pages:
1
2 |
gravityzero
Hazard to Self
 
Posts: 79
Registered: 14-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: forgetful
|
|
Vacuum Distillation Confusion
I would have to say that I'm still very much a beginner. I would like to think I'm getting better, but scenarios such as what happened tonight prove
otherwise.
Recently I've notice that during vacuum distillation, I don't get that much lower of a boiling point separation, as would normally be expected. I've
attributed this to not putting sufficient grease at the joints.
Tonight I decided to vacuum distill water and see if I could get better results by greasing the joints more. So I added a nice even layer of grease
at every joint.
The water was able to boil at under 50C at 23in Hg. The boiling point seems lower, but now I get an inconsistent drip rate. I will get like 5 quick
drips, then nothing for 30secs, then a few more quick drips.
This went on and on, no matter what I did. I would increase temperature, but nothing better would happen. I increased temps drastically, but still
no steady drip rate.
A few drips would come over together, then nothing. I can see, what looks to be air entering into the top joint of the condenser.
The only thing I can figure is this could be causing a negative vacuum, preventing a steady drip rate.
Has anyone encountered similar? I mean, I've vacuum distilled before and I don't recall all the hassle. I spent like over two hours trying to vacuum
distill like 100ml of water.
|
|
|
TheChemiKid
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 493
Registered: 5-8-2013
Location: ̿̿ ̿̿ ̿'̿'̵͇̿̿з=༼ ▀̿̿Ĺ̯̿̿▀̿ ̿ ༽
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
First off: This should have been posted in Beginnings.
Here is a probable answer to your question: If your vacuum pump is a rather cheap pump, the vacuum will almost definitely fluctuate a lot during the
distillation. Even very expensive diaphragm pumps can still fluctuate slightly.
When the police come
\( * O * )/ ̿̿ ̿̿ ̿'̿'̵͇̿̿з=༼ ▀̿̿Ĺ̯̿̿▀̿ ̿ ༽
|
|
|
gravityzero
Hazard to Self
 
Posts: 79
Registered: 14-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: forgetful
|
|
The pump is fairly expensive. It is a rocker 500 and it seems consistent with the vacuum, at least from the gauge at the vacuum.
Should I be striving for absolutely no leaks in a vacuum distill?
At such high vacuum, should I be using something besides Vaseline to grease?
I've seen things like "Dow High Vacuum Grease", I just didn't think it was a must.
|
|
|
BromicAcid
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3254
Registered: 13-7-2003
Location: Wisconsin
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rock n' Roll
|
|
First set of questions. What kind of trap are you using? Are you cooling your receiver? What kind of condenser do you have in line? If you are not
condensing the vapors and keeping them condensed, put another way, if the vapors are making their way to the vacuum pump, then you will see these
surges. In these cases the system is being pulled under vacuum by removing the gases in the system. The material begins to distill, vaporizing and
turning into a gas, this new gas fills the system. When this gas does not condense then the pressure in your system goes up, the distillation stops,
and the pump has to work again to remove this gas to get the pressure back down and the cycle repeats.
Edit: If you are able to measure the vacuum (since you mention you had a reading of 23 inches of mercury) simply measure the vacuum on the pump itself
with the pump not connected to anything. Now assemble the glassware without anything in it but properly greased. Connect the pump to the setup and
allow it to pull down for 10-30 minutes, now measure the vacuum on the setup, A properly greased and sealed setup should give an identical reading to
the pump on itself.
Edit 2: You said you were boiling water at 50C and 23 in Hg, when I used the nomograph on that value I see you were still supposed to be boiling in
the 90's. To boil even in the 50C range you're going to need pressures of ca. 4-5 inHg. Something would have to be notably wrong to get these sorts
of values with a decent vacuum pump, I don't think you would be losing this much due to leaking joints, and you should hear any sort of leak. Then
again maybe your vacuum gauge is wrong.
[Edited on 1/11/2014 by BromicAcid]
|
|
|
TheChemiKid
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 493
Registered: 5-8-2013
Location: ̿̿ ̿̿ ̿'̿'̵͇̿̿з=༼ ▀̿̿Ĺ̯̿̿▀̿ ̿ ༽
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
You should definitely invest in some Dow High Vacuum Grease. It will last you a long time, and is very chemically resistant. For almost any
distillation, this is a must. Even though it is expensive, a little bit goes a long way.
When the police come
\( * O * )/ ̿̿ ̿̿ ̿'̿'̵͇̿̿з=༼ ▀̿̿Ĺ̯̿̿▀̿ ̿ ༽
|
|
|
gravityzero
Hazard to Self
 
Posts: 79
Registered: 14-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: forgetful
|
|
Thanks for the comments.
Bromic, I'm doing this as a test with water and I'm using a very simplistic vacuum distillation setup.
I'm using a 250ml boiling flask, connected to a 3-way adapter, connected to a 200mm liebig condenser, connected to a vacuum adapter, connected to a
collection flask.
I'm trying this again as I type. I have the vacuum wide open and the vacuum is causing the water to boil at around 43C. For this to happen, it is a
certain that the vacuum is working.
The vacuum gauge measures a kPa value of 90, which converts to roughly 26inHg.
The distillate condenses, and at this stage there is no trap being used. The vacuum itself has a built in moisture trap that does not appear to be
collecting any vapor.
After resealing the joints this morning, I no longer see bubbles at any of them. I allowed the vacuum to set for a few minutes before I proceeded to
distill and I think that helped.
I am still getting a very inconsistent drip rate. I will get maybe 5 drips to come over at once, then nothing for better part of a minute, then 5
more drops, then nothing.
When distilling at normal pressure, I can always obtain a steady and consistent drip rate.
I feel like the condenser is working correctly. I don't think any vapor is escaping, but I have had that occur in the past.
I also think the product being distilled is just as clean, it is just unpredictable and takes forever.
|
|
|
BromicAcid
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3254
Registered: 13-7-2003
Location: Wisconsin
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rock n' Roll
|
|
Again, something is wrong with the data you are giving. By the pressure provided your water should be boiling in the 90s, at the temperatures you
provided your vacuum should be in the ballpark of 13 kPa (since your vacuum is reading in kPa). Actually... atmospheric pressure is about 101 kPa,
you're reading 90 kPa... does the scale read zero at atmospheric pressure? Is it showing the pressure drop as say -90 kPa in which case the actual
pressure would be around 10 kPa which would at least make sense with the rest of it.
My suggestion still holds, empty out the water, dry your glassware, and vacuum check the setup. If your setup holds vacuum without the water then
your issue is that you are not condensing the vapors and it is killing your vacuum. Just because there is a water trap doesn't mean it will remove
gross water contamination.
|
|
|
gravityzero
Hazard to Self
 
Posts: 79
Registered: 14-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: forgetful
|
|
You are correct to say -90kPa. Sorry for not posting the negative, but a vacuum distillation will always be done at reduced pressure.
I will try this later with a 400mm liebig and see if it gets any better.
I know what you are getting at and I've had vacuum distillations in the past where vapor was noticeably escaping the setup.
If it ain't one thing it's another. I appreciate all comments and I will press on.
Hopefully I haven't caused permanent damage to the vacuum.
Thank you BromicAcid for all your assistance.
|
|
|
BromicAcid
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3254
Registered: 13-7-2003
Location: Wisconsin
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rock n' Roll
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by gravityzero  | | You are correct to say -90kPa. Sorry for not posting the negative, but a vacuum distillation will always be done at reduced pressure.
|
Yes, it is valid to say that a vacuum distillation will always be done under reduced pressure however in literature you will not see negative values
for pressure in literature or even on this site. Atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa, not zero. Your reading of -90 kPa should be subtracted from this
value to give your actual pressure of 11 kPa. -90 is just confusing, the only time I see negative numbers with pressure involve PSI, there is a PSIA
where the value starts at 0 (absolute vacuum) and a PSIG where 0 is actually atmospheric pressure. But even they are differentiated by a difference
in units to avoid ambiguity.
|
|
|
S.C. Wack
bibliomaster
    
Posts: 2419
Registered: 7-5-2004
Location: Cornworld, Central USA
Member Is Offline
Mood: Enhanced
|
|
That's about how it is, though I'd say you need to either turn up the heat or the vacuum a little if you want things to go faster; it's a solid rule
IMHO. A lot of this has to do with condensate buildup in the apparatus more than anything with my apparatus, but in general weird little pressure
swings should occur in the condenser especially; raw imperfect equilibrium between liquid and gas and heat and suddenly things condense if your
condenser can handle it. Given how violent things are in the pot, it shouldn't be too surprising.
|
|
|
Panache
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1290
Registered: 18-10-2007
Member Is Offline
Mood: Instead of being my deliverance, she had a resemblance to a Kat named Frankenstein
|
|
My first thought was that you're simply at the mercy of superheating/bumping, something exacerbated under reduced pressure. A push pull circumstance
can ensue.
A really good exercise that helps one understand how dynamic and oscillating the pressure gradients within a distillation setup are is to setup for a
vacuum distillation, using water, without connecting the vacuum hose. Then begin the distillation and get it running at a even constant rate. Then
place a small balloon over the vacuum outlet on the setup.
You will notice an oscillation within the balloon.
Back to point, stir your boiling water or put some pumice, boiling stones or best yet a capillarily to the bottom of the flask that allows slight air
ingress.
|
|
|
Oscilllator
National Hazard
   
Posts: 659
Registered: 8-10-2012
Location: The aqueous layer
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I have a different idea as to what might be the problem with regards to inconsistent dripping. Perhaps a little of the grease you applied to the
joints found its way inside the glassware, leading to a band of grease around the inside of the joint. Because grease is hydrophobic, perhaps the
water slid down the condensor and was stopped by the band of grease until sufficient water had built up to overcome the repellent force the grease
provided.
Once that force had been overcome, all the water that had built up behind the grease (several drips worth at least) would flow over the grease and
into the condensor, and the cycle would start again
|
|
|
Magpie
lab constructor
    
Posts: 5939
Registered: 1-11-2003
Location: USA
Member Is Offline
Mood: Chemistry: the subtle science.
|
|
I've run several vacuum distillations during various syntheses. I remember some pressure fluctuations but not to where it was overly objectionable.
If your vacuum source is an aspirator variation in water pressure would result in vacuum fluctuation.
If your surging is caused by fluctuations in the vacuum source you could try adding a "vacuum reservoir" to your system. This could be any relatively
large vessel, such as a 1-liter Buchner filter flask, that is capable of full vacuum. This could be teed into your system with a piece of vacuum
hose.
The single most important condition for a successful synthesis is good mixing - Nicodem
|
|
|
gravityzero
Hazard to Self
 
Posts: 79
Registered: 14-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: forgetful
|
|
The water did appear to be bumping somewhat. It was being stirred and even had a boiling stone, but it still appeared to be having trouble boiling
properly. I've also read that insulating the boiling flask might help.
I'm trying to understand the core concepts and avoid just getting it to work. I'm using the same methodology for determining condenser length.
My understanding is the higher the boiling point, the shorter the condenser.
I've seen materials with atmospheric boiling points above 200C being distilled without a condenser and assumed this was the reasoning.
|
|
|
S.C. Wack
bibliomaster
    
Posts: 2419
Registered: 7-5-2004
Location: Cornworld, Central USA
Member Is Offline
Mood: Enhanced
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by gravityzero  | | The water did appear to be bumping somewhat. It was being stirred and even had a boiling stone, but it still appeared to be having trouble boiling
properly. |
Another guess the unprovided detail thread then. In that case, you're not getting condensate because you're not getting evaporation except on
superheating. Plus: is that stirring...magnetic? Magnetic stirring and a boiling stone for this? BTW...no one can see air enter clean undamaged very
lightly greased tapered joints, unless whoever finished the glass was Chinese or tripping balls...water really is suckier than other solvents to
distill...use the same grease everyone else does, to fit in if nothing else.
It should not be "bumping somewhat", it should be bumping constantly and unambiguously, unless the flask is rotating or stirred hard overhead.
There may be some practical reason why 95% of organic chemistry books have capillary tubes coming in from the top or through an extra neck as the #1
option. IMHO ghetto means borosilicate tubing that barely fits though a thermometer joint, a blowtorch, scissors, and electrical and/under teflon
tape, and humbly suggest giving something along those lines a go.
|
|
|
testimento
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 351
Registered: 10-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I have a question regarding the boiling points and pressure. I have vacuum pump that generates quite hard vacuums, as low as sub-millibar scale,
according to the factory. I haven't tested it though, but I though that if I have high boiling liquids, like 150-300C, is the boiling point of the
liquids linear? A calculator dictates that a liquid boiling 200C will boil at whopping -70C when using sub-millibar vacuum. This causes problems with
condensation, of course.
So, do I need to get vacuum regulator, or are there some physical laws regarding the boiling points at very low pressures that interfere with this
calculation? I've heard that water doesn't actually boil at very low pressures at less than -50C or something. Is this true?
|
|
|
BromicAcid
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3254
Registered: 13-7-2003
Location: Wisconsin
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rock n' Roll
|
|
Look up a nomograph and you will be able to correlate reduced pressure to boiling point. You do not need a vacuum regulator so much as just a way to
bleed air or better yet nitrogen into the system to help keep the vacuum consistent. Never heard of water not boiling well at low pressures though.
|
|
|
testimento
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 351
Registered: 10-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
What I was trying to say is this:
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/08/Ph...
That water exists only in solid and will not evaporate at certain temps and pressures? Does this kind of action apply to other stuff too?
|
|
|
BromicAcid
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3254
Registered: 13-7-2003
Location: Wisconsin
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rock n' Roll
|
|
As a distillation progresses it requires a constant input of heat to replace the energy lost of components distill out of the system. If you had
water under full vacuum and were really ripping it out of the system, faster than you were even putting energy in, and the pot kept getting cooler
your distillation will slow because your system does not have much energy, but you will still be pulling off water. Your other issue will be your
heat transfer will not be as good as the water solidifies. The only difference through is that you will not have a liquid phase, you will be
subliming your water instead of distilling your water, but that does not magically mean that water will stop being removed from the system.
|
|
|
testimento
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 351
Registered: 10-6-2013
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Well, then I've gotta get the manual valve to adjust the pump capacity directly. 
|
|
|
organicchemist25
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 136
Registered: 12-2-2014
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I see this thread is current, so I am hoping someone would help clarify something. I have done searching on here and the web and various organic
literature, including Vogel and Zubrick.
Here is my question. And basically a yes or no answer will give me the answer I need to move forward.
When I hook up and prepare for vacuum distillation, do I seal the system completely up(which seems so wrong). or do I have a slight bit of air (or gas
if needed) controlled by something like the hoffman clamp on a hose or valve shut off on one of the glass joints of the flask ? I feel it needs to let
a tiny bit of either air or gas in, as vacuum is being applied to it.
Here is some pics of the lab, since I think this is my first post. I have used this site for a lot of answers I was looking for. I hope to be able to
repay by providing relative info to help others out.
I have a corning hot plate and stirrer, I have a single stage pump, as well as an aspirator, high vacuum joint grease and a Meriam Instrument digital
manometer. I also have a Hoffman style hose clamp if I need it to regulate the input of outside air or a gas. I have had first semester Organic, but
know quite a bit more than that from my own reading and experimenting.
Vacuum distillation is about the only practice I am not knowledgeable in at my current level of experience. I really want to to get comfortable and
experienced with it.
We NEVER did a vacuum distillation in my lab. I even asked my prof about vacuum distillation and they really couldnt answer my question.
And any additional info or tips would be greatly appreciated.
And if someone could identify the glass apparatus I am holding? I have no idea what it is and what it might be used for. I was told it was a custom
piece when I bought it.
Thanks.
       
|
|
|
S.C. Wack
bibliomaster
    
Posts: 2419
Registered: 7-5-2004
Location: Cornworld, Central USA
Member Is Offline
Mood: Enhanced
|
|
There are vacuum controllers my favorite being the faucet. Next favorite: not tightening the connection of the pump that tight. Not sure what's wrong
with full vacuum. If you're going to run air or whatever in the system might as well run it through a not so fine capillary to the bottom of the
liquid. Maybe this is faster than standard vacuum distillation if the vacuum, heating, and cooling are up to it?
But one may often regulate heat instead of vacuum.
[Edited on 17-2-2014 by S.C. Wack]
|
|
|
sbreheny
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 145
Registered: 30-1-2014
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by organicchemist25  | I see this thread is current, so I am hoping someone would help clarify something. I have done searching on here and the web and various organic
literature, including Vogel and Zubrick.
Here is my question. And basically a yes or no answer will give me the answer I need to move forward.
When I hook up and prepare for vacuum distillation, do I seal the system completely up(which seems so wrong). or do I have a slight bit of air (or gas
if needed) controlled by something like the hoffman clamp on a hose or valve shut off on one of the glass joints of the flask ? I feel it needs to let
a tiny bit of either air or gas in, as vacuum is being applied to it.
Here is some pics of the lab, since I think this is my first post. I have used this site for a lot of answers I was looking for. I hope to be able to
repay by providing relative info to help others out.
I have a corning hot plate and stirrer, I have a single stage pump, as well as an aspirator, high vacuum joint grease and a Meriam Instrument digital
manometer. I also have a Hoffman style hose clamp if I need it to regulate the input of outside air or a gas. I have had first semester Organic, but
know quite a bit more than that from my own reading and experimenting.
Vacuum distillation is about the only practice I am not knowledgeable in at my current level of experience. I really want to to get comfortable and
experienced with it.
We NEVER did a vacuum distillation in my lab. I even asked my prof about vacuum distillation and they really couldnt answer my question.
And any additional info or tips would be greatly appreciated.
And if someone could identify the glass apparatus I am holding? I have no idea what it is and what it might be used for. I was told it was a custom
piece when I bought it.
Thanks.
|
Wow, what a beautiful home lab! Is that a fume hood? Is this structure built inside a garage? Is that a dehumidifier I see there in the corner?
As for vacuum distillation I *believe* that there is not necessarily a need to allow air into the setup, unless you want a slightly higher pressure in
the setup than the minimum your vacuum pump will produce. Beware, too, that you need some kind of trap between your distillation apparatus and your
vacuum pump - especially if the pump is not a specialized chemical-resistant one. It's typical to have a desiccant tube in line with the pump along
with something to catch particulates or large drops of liquid which can be accidentally ingested (this will often be simply a container which draws
gas from the setup through a tube which opens at the bottom of a receiving vessel and then connects the vacuum pump near the top so that a few
droplets are not likely to get sucked all the way through). For organic vapors, this same kind of setup is often cooled down by an alcohol/dry-ice
mixture or even LN2 to form a cold trap to condense the vapor very quickly before it can make it through into the pump. Beware that using LN2
absolutely requires that the entire apparatus be free of air or other oxygen sources as LOX will condense at LN2 temperature and react explosively
with anything flammable.
Finally, beware of implosion hazard with vacuum. Vacuum-rated glassware is typically quite a bit thicker-walled. Even with special glassware (and
especially if you are doing this with normal glassware - but never with the really thin-walled cheap stuff!), you should have an additional layer of
implosion protection such as a polycarbonate shield or mesh around each piece of glassware.
|
|
|
Panache
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1290
Registered: 18-10-2007
Member Is Offline
Mood: Instead of being my deliverance, she had a resemblance to a Kat named Frankenstein
|
|
Why is it you feel you require an air bleed, this seems contrary to the entire concept of vacuum distillation. To control the vacuum having a needle
valve t-pieced into the line as close to the pump as possible is the simplest solution, variously sophisticated manostats being the least simple.
Only pull a decent vacuum on spheres, tubes, pears and their interconnecting paraphernalia unless the item is specially strengthened for vacuum (such
as vacuum flasks for Büchner funnels). Schott laboratory reagent bottles can also take a full vacuum.
My one implosion on a two litre erlenynmer, where I mistakenly became distracted and the slight vacuum I was using to draw away some evolved gases
went deeper than expected as the gases stopped evolving has scarred me forever. The sound/boom was odd and the 1000ml or so of solvent and slight
lacryomater went over everything within three metres.
Luckily my back was turned!
|
|
|
organicchemist25
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 136
Registered: 12-2-2014
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Thank you everyone for replying.
I do have a solvent trap and a inline vacuum trap for when I hook up the vacuum.
That is a A/C and dehumidifier combo.
I guess the reason why I was think about letting just a tiny bit of air or gas in is so that is was never a closed system. I have seen pics that had
a needle tip submerged with tiny bubbles in the solution. I just figured, obviously the vacuum would be a lot higher than the tiny amount being input
onto the system. I will attach a pic or two that I have seen that gave me the assumption at one time about letting air/gas into the system.
I have never been able to find a solid reference as to what I was looking for. Maybe I have been over thinking it. I just definitely what to have a
good understanding and what exactly I have to do to do it as safe as possible. I do know not to use thin walled and I definitely know the risk of
implosion. That is definitely why I wanted to ask the experienced.
Oh, and can anyone ID that vigreux column and graham condenser combo piece in the last picture I attached? and what it is used for?
Thanks
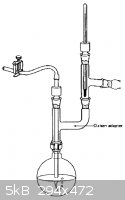 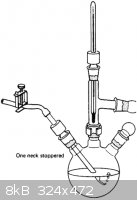
|
|
|
| Pages:
1
2 |