| Pages:
1
2 |
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
Possible Route to Copper Nitrate
I was thinking about copper nitrate 2.5 hydrate as a precursor to fuming nitric acid via the normal acidification due to the obvious ease of
regenerating sulfuric acid from the sulfate byproduct. Even easier perhaps, the nitrate can be decomposed thermally to yield NO2 and O2 for making
nitric acid or other uses. The usual routes of synthesis are not suitable for this of course as they defeat the purpose, either involving nitric acid
itself or its derivatives, or resulting in the very highly stable sulfates I would like to avoid.
Here's my idea. Electolysis with a copper anode in ammonium nitrate solution should normally break down the ammonium salt forming copper nitrate with
liberation of ammonia at the cathode (possibly in a membrane or membraneless cell). However at least two further reactions would prevent this from
yielding any copper nitrate; copper would be electroplated out from copper nitrate at the cathode, and ammonia at the cathode would complex with
copper or copper compounds. To prevent this, I am considering an AC electrolysis process in a hot cell (near 100°C). The alternating current should
disallow any copper from plating out (nitric acid would be retained), and as ammonia is eventually lost to evaporation from both electrodes during the
cathodic period, the composition of the electrolyte should be driven toward copper nitrate.
The concerns I have is that the ammonia will be oxidized, resulting in overall loss of ammonia (which I would like to retain by bubbling into solution
in an adjacent vessel), or complexed with copper resulting in contamination and losses.
In a DC cell with two copper electrodes, where copper is removed from the anode and deposited on the cathode, the electrolyte should still tend toward
copper nitrate as ammonia should still be lost. The process would then be periodically reversed, but the AC electrolysis should take care of that
automatically. The only difference really is the potential for ammonia to be oxidized. I don't really know enough about the chemistry of
ammonia/copper complexes to guess how this would affect the system, but upon boiling the electrolyte to dryness it should be easy to break down those
impurities.
Because of the intended use of the final copper nitrate product, any remaining ammonium nitrate should be removed as well. Of course this is easily
done by heating to decomposition, but the copper nitrate hydrate will decompose as well at those temperatures. I'm not really sure of another way to
remove or destroy remaining ammonium nitrate or determine when there is no more present, except simply decomposing the lot and allowing ammonium
nitrate to reform and solidify in a condenser.
The copper oxide left after the process can be recycled by smelting (even though that is an energy intensive process). Copper oxide could also be
added to excess sulfuric acid used to dehydrate the HNO3, thereby converting it to copper sulfate for reclaimation. Though more tedious, the total
process would allow production of fuming nitric acids without net loss or hydration of sulfuric acid or without requiring the difficult contact
process to reclaim it.
[Edited on 6-3-2008 by kilowatt]
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
12AX7
Post Harlot
    
Posts: 4803
Registered: 8-3-2005
Location: oscillating
Member Is Offline
Mood: informative
|
|
| Quote: | Originally posted by kilowatt
The concerns I have is that the ammonia will be oxidized, resulting in overall loss of ammonia (which I would like to retain by bubbling into solution
in an adjacent vessel), or complexed with copper resulting in contamination and losses. |
Nah, nitrate will be reduced. It would be too easy if ammonia could be oxidized.
Ammonia is too soluble. I don't see any reason why it should leave. Copper will be oxidized at the anode and taken into solution, while nitrate and
H+ will be reduced at the cathode, losing NO3 and causing some alkalinity (the ammonium in solution will buffer the catholyte pH around 8-10). When
the copper and alkali meet, Cu(OH)2 will form, which may dissolve in excess NH3 if you let it run for a really long time. If you use a membrane, this
will not happen, but a buildup of NH3 in the catholyte will reduce conductivity (NH3 doesn't ionize very much in H2O).
A better idea would be to fill the cathode chamber with a conductive, essentially unreactive alkali, like NaOH, placing your nitrate in the anode
chamber. NaNO3 could be used. Na ions migrate to the cathode, so it becomes more basic (and more conductive, not at all a problem), while copper
ions migrate from the anode into the anolyte. Note copper ions will want to migrate out as well; an ion-selective membrane would be great, but I
suppose that's a little too much to ask for! To minimize loss, you'll have to change the anolyte when it's only, say, 10% copper (since the amount of
loss is proportional to the concentration, you should get logistic growth over time) and fumble with it from there.
Tim
|
|
|
not_important
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3873
Registered: 21-7-2006
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Try boiling copper oxide with a strong solution of ammonium nitrate, skip the electrolysis.
|
|
|
The_Davster
A pnictogen
      
Posts: 2861
Registered: 18-11-2003
Member Is Offline
Mood: .
|
|
Could use electrolysis for the synthesis of the copper oxide; I have. Copper anode and cathode, KNO3 electrolyte with good stirring. Copper
hydroxide initially forms but the cell resistively heats to the point of decomposing it to the oxide.
Extended cell runs cause loss of nitrate by reduction to ammonia.
Tim's Idea separating anolyte and catholyte would work, but would take a long time. I have found it very difficult to obtain synthetically useful
currents in such cells, especially with improvised membranes.
|
|
|
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
| Quote: |
Try boiling copper oxide with a strong solution of ammonium nitrate, skip the electrolysis. |
How would that work? Copper oxide is insoluble and both it and ammonium nitrate are far more stable than copper nitrate.
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
not_important
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3873
Registered: 21-7-2006
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
NH4NO3 <=> NH3 + HNO3 (far to the left, but concentrated solutions have pH 4 to 6)
Some of the ammoniua is sweep away with the steam, lthis also works with ammonium sulfate but gives NH4HSO4.
Try it, let maybe a tenth of the water boil away before replacing it, repeat several times. Works even better with carbonates.
Actual molten ammonium salts work better, and have been used as replacements for the corresponding acids when concern over acid leaks was important -
field analysis kits for mineralogy back per-WWII and thus pre-flexi-plastics.
However as the decomposition temperature of cupric nitrate is about the same as the melting point of ammonium nitrate, who's own decomposition
temperature isn't much higher, it's not likely to be useful preparatively.
|
|
|
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
I know for a fact molten ammonium nitrate likes to decompose to H2O + N2O instead of the HNO3 + NH3 that I would prefer. Evidently this is not the
same as in the boiling solution you describe?
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
12AX7
Post Harlot
    
Posts: 4803
Registered: 8-3-2005
Location: oscillating
Member Is Offline
Mood: informative
|
|
NH3 passing off as gas is the driving force. NH3 + CO2 boils off easier, hence the carbonate suggestion. CuO isn't very basic, so it's going to go
slowly. Carbonates usually react faster (I would imagine the mildly acidic pH would help bring some into solution), and ammonium bicarbonate is a
more favorable "leaving group".
Tim
|
|
|
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
I had thought briefly about copper hydroxide but did not think the reaction would proceed. Are you suggesting copper carbonate and ammonium nitrate
to remove ammonia and CO2 leaving copper nitrate?
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
not_important
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3873
Registered: 21-7-2006
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Well, there is no copper carbonate as such, just basic carbonates. They react faster than the oxide, especially oxide that's been heated to a high
temperature like copper scale.
Anything that drives the reaction balance in the desired direction is good. Boiling to help drive off ammonia, the steam leaving helps carry the
ammonia away so boiling tends to be more effective than heating to just below boiling. Carbonates are better because the CO2 escapes the same way, so
BaCO3 and MnCO3 will react fairly quickly. Strong bases, Ba(OH)2 for example, readily displace the weak base "NH4OH"; with strong bases you often can
get away with a mildly warm solution and bubbling clean air through it to carry away the NH3.
Cu(OH)2 likely works faster than CuO, but you can't heat it much or the hydroxide goes over to the oxide. And you were proposing to make nitric acid
by heating cupric nitrate, which leaves the oxide so a method that cycles between oxide and nitrate seems simpler.
BTW
2Cu(NO3)2 5H2O => 2CuO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g) + 5H2O ==> 4 HNO3 + 3 H2O
(ignoring how you get that to go to completion) limits the concentration of the nitric acid you'll get. It is pretty strong, if you can get close to
that limit you should be happy.
|
|
|
Rosco Bodine
Banned
Posts: 6370
Registered: 29-9-2004
Member Is Offline
Mood: analytical
|
|
How about a double decomposition of copper chloride
with potassium nitrate , extract the dried residue with methanol in which copper nitrate is highly soluble and potassium chloride is not .
|
|
|
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
Thanks for the help, looks like this may be workable.
| Quote: |
2Cu(NO3)2 5H2O => 2CuO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g) + 5H2O ==> 4 HNO3 + 3 H2O
(ignoring how you get that to go to completion) limits the concentration of the nitric acid you'll get. It is pretty strong, if you can get close to
that limit you should be happy. |
Yeah I was going to use concentrated H2SO4 to dehydrate the HNO3 fully, but I was going to then react the left over sulfuric acid solution with the
left over CuO to get CuSO4, which I was going to decompose to SO3 and CuO.
To go from CuO to (CuCO3*Cu(OH)2) is not a big deal really, it can be done with precipitation. Clearly going from CuO to 2Cu(NO3)2.5H2O and back is
simpler though and I doubt going to the trouble of making the carbonate would save any time even if the reaction is much faster, because its
production is itself time consuming.
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
YT2095
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1091
Registered: 31-5-2003
Location: Just left of Europe and down a bit.
Member Is Offline
Mood: within Nominal Parameters
|
|
be very careful with Copper around ammonium nitrate, it can form an unstable salt (tetramine copper 2 nitrate) that can explode!
\"In a world full of wonders mankind has managed to invent boredom\" - Death
Twinkies don\'t have a shelf life. They have a half-life! -Caine (a friend of mine)
|
|
|
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
Any idea how to make that not happen?
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
Nicodem
Super Moderator
      
Posts: 4230
Registered: 28-12-2004
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Once that I needed some copper(II) nitrate whatever hydrate I prepared it by dissolving some copper wire in dillute HNO3 with stoichiometric H2O2
added (I was a bit stingy on HNO3). I remember that after I had evaporated and recrystalized it and was vacuum filtering it, I thought it would be
good to wash the remains of water from the crystals by washing with acetone so it would dry rapidly. What a stupid thing to do! To my surprise I
learned that copper(II) nitrate is well soluble in acetone.
|
|
|
Aqua_Fortis_100%
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 302
Registered: 24-12-2006
Location: Brazil
Member Is Offline
Mood: †
|
|
| Quote: | Originally posted by YT2095 :
be very careful with Copper around ammonium nitrate, it can form an unstable salt (tetramine copper 2 nitrate) that can explode!
|
What?!
Some persons says that this is a "primary" explosive , but honestly I never had any good results with it ! I make some grams of it a long time ago
with some fine Cu powder in NH4NO3 boiling solution + NH3 and precipitating with alcohol.. Drying well.. with a match flame a small amount merely make
a 'puff' with more than 10-20 seconds of strong heating.. Pretty insensitive!
(Actually I think it is only dangerous as contaminant for ammonium nitrate based explosives and some others)
NH4NO3 + Cu oxide/carbonate would be the way to go to copper nitrate.. Another , maybe better route would be CuSO4 and Ca(NO3)2 ..
Here Ca(NO3)2 is hard to find as agricultural supplement but is easily made from NH4NO3 + lime..
"The secret of freedom lies in educating people, whereas the secret of tyranny is in keeping them ignorant."
|
|
|
YT2095
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1091
Registered: 31-5-2003
Location: Just left of Europe and down a bit.
Member Is Offline
Mood: within Nominal Parameters
|
|
it`s still an undesirable product that present a potential Danger (not to mention legalities).
for this Not to be presented would be negligent!
\"In a world full of wonders mankind has managed to invent boredom\" - Death
Twinkies don\'t have a shelf life. They have a half-life! -Caine (a friend of mine)
|
|
|
TheApplianceOfScience
Harmless

Posts: 2
Registered: 3-3-2008
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
How about adding an excess of Cu metal to dilute (38%) nitric acid, filtering under suction to remove unreacted Cu and other insoluble junk, then
evporate until crystals form? I've tried it; it works! Just beware of the noxious fumes of NO2- literature states that only concentrated nitric acid
produces brown NO2 fumes; but from my experience, even dilute (38%) nitric acid produces NO2 when it reacts with Cu.
|
|
|
YT2095
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1091
Registered: 31-5-2003
Location: Just left of Europe and down a bit.
Member Is Offline
Mood: within Nominal Parameters
|
|
actually I process All my scrap copper in this way, I save it all up in a jar and when I have a good 500g or so, I dissolve the lot in 38% Nitric with
copper in excess.
then I convert it all to the Carbonate and store it in a jar.
from this point I can make any simple copper salt I like with ease.
\"In a world full of wonders mankind has managed to invent boredom\" - Death
Twinkies don\'t have a shelf life. They have a half-life! -Caine (a friend of mine)
|
|
|
Nicodem
Super Moderator
      
Posts: 4230
Registered: 28-12-2004
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
| Quote: | Originally posted by TheApplianceOfScience
Just beware of the noxious fumes of NO2- literature states that only concentrated nitric acid produces brown NO2 fumes; but from my experience, even
dilute (38%) nitric acid produces NO2 when it reacts with Cu. |
Dissolution of copper in dilute HNO<sub>3</sub> produces NO, a colorless gas that immediately oxidizes to NO<sub>2</sub> upon
contact with atmospheric oxygen. More concentrated HNO<sub>3</sub> reduces mostly only to NO<sub>2</sub> during the oxidation
of copper. By adding H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> you get a dissolution with nearly no gas formation until all the peroxide gets
consumed. Also, as a consequence you need less HNO<sub>3</sub> to dissolve the same amount of copper (see the appropriate redox
equations).
Atached (I have not read it, but I guess it is relevant even though ancient):
The Conditions of the Reaction between Copper and Nitric Acid
V. H. Veley
Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 46 (1889) 216-222
[Edited on 7/3/2008 by Nicodem]
Attachment: The Conditions of the Reaction between Copper and Nitric Acid.pdf (529kB)
This file has been downloaded 1287 times
|
|
|
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
| Quote: |
How about adding an excess of Cu metal to dilute (38%) nitric acid, filtering under suction to remove unreacted Cu and other insoluble junk, then
evporate until crystals form? I've tried it; it works! Just beware of the noxious fumes of NO2- literature states that only concentrated nitric acid
produces brown NO2 fumes; but from my experience, even dilute (38%) nitric acid produces NO2 when it reacts with Cu. |
I am trying to make nitric acid in the first place here from ammonium nitrate using a cyclic process, not the other way around. For me this is better
than the acidifying an alkali nitrate because I do not have a huge supply of sulfuric acid to just be using up.
[Edited on 7-3-2008 by kilowatt]
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
Formatik
National Hazard
   
Posts: 927
Registered: 25-3-2008
Member Is Offline
Mood: equilibrium
|
|
Why not just heat inorganic copper salts with a nitrate? Heating under a low flame (bunsen burner) a mixture of CuSO4. 5 H2O with KNO3 turns green and
then forms brown nitrogen oxides, leaving a black residue.
|
|
|
kilowatt
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 322
Registered: 11-10-2007
Location: Montana
Member Is Offline
Mood: nitric
|
|
I am trying to find a route that uses ammonium nitrate specifically because that's what I have most of, releases ammonia for collection, and does not
produce any alkali metal salts of sulfuric acid (which are relatively difficult to recycle). The reaction of of CuSO4. 5 H2O with KNO3 would require
first the reaction of KOH or NaOH with ammonium nitrate to produce said nitrate, and then the production of K2SO4 or NaSO4 by CuSO4 which ultimately
uses up copious amounts of sulfuric acid by converting it to a relatively irrecoverable form.
I thought that's what I tried to convey with my last post but here I am repeating myself...
I am trying to find overall reactions that simply produce nitric acid and ammonia from ammonium nitrate without using up anything else, not trade one
acid for another. Copper salts probably aren't the way to go after all (TACN can be produced), but I am looking at possible lead, aluminum, and
magnesium routes involving electrolysis or amalgam electrolysis in other threads.
I think we all know how to produce Cu(NO3)2 or NO2/O2 for their own sake, and thanks for the additional route  but this is a different process. but this is a different process.
[Edited on 10-8-2008 by kilowatt]
The mind cannot decide the truth; it can only find the truth.
|
|
|
Formatik
National Hazard
   
Posts: 927
Registered: 25-3-2008
Member Is Offline
Mood: equilibrium
|
|
The mods should remove those posts. I will start another thread on this, since I haven't seen this discussed.
|
|
|
franklyn
International Hazard
    
Posts: 3026
Registered: 30-5-2006
Location: Da Big Apple
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
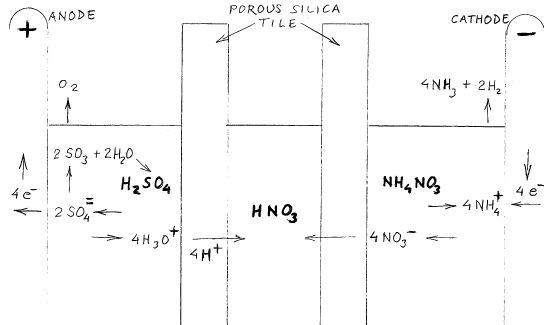
Nitric Acid Bridge - Voltaic Cell
This thread is misnamed and meandered far afield from the propsed premise,extracting nitric acid
from ammonium nitrate. I don't know if this can be made to work but it seems to me that a voltaic
cell can serve this purpose. The interfacing reservoir collects concentrated nitric acid and serves
for what is normally the connecting salt bridge.
|
|
|
| Pages:
1
2 |