Jackson
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 189
Registered: 22-5-2018
Location: U S of A
Member Is Offline
Mood:  Happy about new glassware 
|
|
Uranium ore tests
Hi, i have a sample of what I belive to be carnotite that i have partially desolved in nitric acid (~20-30%) it is not completely desolved because I
didn’t make enough acid (i was using a small ammount of leftover acid from a cellulose nitration). I know uranyl nitrate glows under blakc light but
i am not able to get one for a while. Is there any other ways to determine if there is uranium content in it other than a black light?
Thanks,
Jackson
|
|
|
12thealchemist
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 181
Registered: 1-1-2014
Location: The Isle of Albion
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rare and Earthy
|
|
The old-school analytical tests (now hobby chem) from my analysis table book for uranium are:
Solutions of uranyl salts treated with ammonia or sodium hydroxide precipitate sparingly soluble uranates.
Potassium ferrocyanide precipitates brown uranyl ferrocyanide in acetic acid solution, the precipitate dissolving readily in hydrochloric acid.
|
|
|
Jackson
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 189
Registered: 22-5-2018
Location: U S of A
Member Is Offline
Mood:  Happy about new glassware 
|
|
Alright. My plan will be to filter out the solids, then precipitate with a base. The urante should look yellow right? My auestion is, will the
vanadates also precipitate? Will they make it harder to determine if uranium is there?
Thanks,
Jackson
|
|
|
12thealchemist
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 181
Registered: 1-1-2014
Location: The Isle of Albion
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rare and Earthy
|
|
Which vanadium species you get is very pH dependent. Vanadates are notorious for forming aggregatory polymeric species. Pourbaix diagrams can be
helpful here. It appears from the diagram below that at high pH, the vanadates should stay in solution.
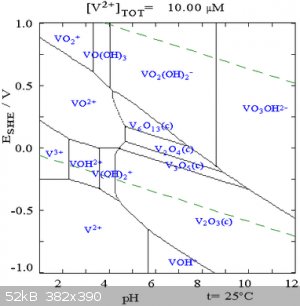
Diagram from Wikipedia
[Edited on 13-12-2018 by 12thealchemist]
|
|
|
Jackson
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 189
Registered: 22-5-2018
Location: U S of A
Member Is Offline
Mood:  Happy about new glassware 
|
|
I have another problem. I no longer belive it is a carnotite ore but rather a zippeite ore.
It matches much better than carnotite. I will upload photos when I get home. It encrusts on the rock rather than being in the rock. There is also a
deposit of zippeite near where i found the ore (Mindat link of the deposit near the location: https://www.mindat.org/loc-210847.html). My question is, in some publications, it says it is often found in association with uranopilite, which is
water soluble. I can not find anything that says it itself is water soluble but I belive it to be so. It says it forms efflorescent encrustations
which are encrustations of water soluble salts but i cannot find anything on its solublilty. Does anyone know what zippeite’s solubility is? Is the
precipitation of uranyl compounds by a hydroxide still viable with it?
Thanks,
Jackson
(Edited for spelling)
[Edited on 12/13/2018 by Jackson]
|
|
|
Jackson
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 189
Registered: 22-5-2018
Location: U S of A
Member Is Offline
Mood:  Happy about new glassware 
|
|
I have found that at room tempature (25 C) zippeite has a solubility of 0.486295315308 grams per liter. It looks like it would be better to dissolve
in acid than water.
|
|
|
DoctorOfPhilosophy
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 130
Registered: 12-6-2012
Location: Ontario, Canada
Member Is Offline
Mood: enthralled
|
|
Holy cow that's a lot of significant digits.... They are all significant right?
On the topic of significant digits: "According to Jörg Arndt and Christoph Haenel, thirty-nine digits are sufficient to perform most cosmological
calculations, because that is the accuracy necessary to calculate the circumference of the observable universe with a precision of one atom."
[Edited on 13-12-2018 by DoctorOfPhilosophy]
|
|
|
Jackson
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 189
Registered: 22-5-2018
Location: U S of A
Member Is Offline
Mood:  Happy about new glassware 
|
|
Here’s the picture of the ore sample

|
|
|
CharlieA
National Hazard
   
Posts: 646
Registered: 11-8-2015
Location: Missouri, USA
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by DoctorOfPhilosophy  | Holy cow that's a lot of significant digits.... They are all significant right?
On the topic of significant digits: "According to Jörg Arndt and Christoph Haenel, thirty-nine digits are sufficient to perform most cosmological
calculations, because that is the accuracy necessary to calculate the circumference of the observable universe with a precision of one atom."
[Edited on 13-12-2018 by DoctorOfPhilosophy] |
My thoughts exactly about significant figures! When I was in college, I can't recall if I ever dealt with more than 4 SF's in lab (classwork is
different). And now I try my best to get 3 and am ecstatic to get 4!
|
|
|
Jackson
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 189
Registered: 22-5-2018
Location: U S of A
Member Is Offline
Mood:  Happy about new glassware 
|
|
After some testing, I think it is a zippeite species of ore. How could I go about extracting this into a soluble compound. I don’t currently have
access to HCl because it is out of stock near me but could I use a mixture of sodium bisulfate and table salt to generate it and dissolve the ore with
that?
|
|
|
fusso
International Hazard
    
Posts: 1922
Registered: 23-6-2017
Location: 4 ∥ universes ahead of you
Member Is Offline
|
|
Why is U associated with V in ores/minerals? What relationship do they have?
|
|
|
12thealchemist
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 181
Registered: 1-1-2014
Location: The Isle of Albion
Member Is Offline
Mood: Rare and Earthy
|
|
Uranates and vanadates both have the capability of forming complex anionic structures; the main group equivalent are the aluminosilicates. Uranium was
once grouped with chromium, molybdenum, and tungsten prior to the invention(!) of the actinide series. I don't know if vanadium and chromium associate
in minerals, however.
|
|
|