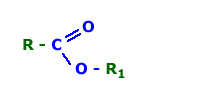
esters
Compounds formally derived from an oxoacid RkE(=O)l(OH)m, (l ≠ 0) and an alcohol, phenol, heteroarenol, or enol
by linking with formal loss of water from an acidic hydroxy group of the former and a hydroxy group of the latter. By extension acyl derivatives of
alcohols, etc. Acyl derivatives of chalcogen analogues of alcohols (thiols, selenols, tellurols) etc. are included. E.g. R'C(=O)(OR) , R'C(=S)(OR) ,
R'C(=O)(SR) , R'S(=O)2(OR) , (HO)2P(=O)(OR) , (R'S)2C(=O) , ROCN (but not R–NCO ) (R ≠ H).
Note:
O-Alkyl derivatives of other acidic compounds [see amides (1)] may be named as esters but do not belong to the class esters proper. E.g. (Ph)2POCH3
methyl diphenylphosphinite.
cited from the IUPAC Gold Book |