Benzophenone
From Sciencemadness Wiki
 |
This article is a stub. Please help Sciencemadness Wiki by expanding it, adding pictures, and improving existing text.
|
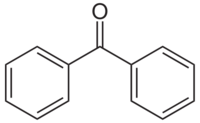
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diphenylmethanone
| |
| Other names
Benzophenone
Diphenyl ketone Benzoylbenzene Benzoylphenyl Diphenylmethanone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 119-61-9 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10O | |
| Molar mass | 182.22 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.11 |
| Melting point | 48.5 °C (119.3 °F; 321.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 305.4 °C (581.7 °F; 578.5 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Benzophenone is the simplest di-aryl ketone.
It is often used in drying solvents together with sodium metal.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Benzophenone can be reduced by sodium metal to produce the intensely blue coloured benzophenone ketyl radical. This is highly reactive towards water and oxygen so it can be used as an indicator of solvent dryness.
Benzophenone is a strong UV absorber, owing to cross-conjugation. This results in its use as a UV photoinitiator in some UV curing resins. Derivatives of benzophenone are often used in sunscreens and as an additive to prevent the UV-induced degradation of polymers.
Physical
White solid
Availability
Available from lab suppliers.
Preparation
Delete this section if not applicable