Difference between revisions of "Salicylic acid"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Chembox | |
| + | | Name = Salicylic acid | ||
| + | | Reference = | ||
| + | | IUPACName = 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid | ||
| + | | PIN = | ||
| + | | SystematicName = | ||
| + | | OtherNames = 2-Carboxyphenol<br>O-Carboxyphenol<br>O-hydroxybenzoic acid | ||
| + | <!-- Images --> | ||
| + | | ImageFile = | ||
| + | | ImageSize = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt = | ||
| + | | ImageName = | ||
| + | | ImageFile1 = Sali22.jpg | ||
| + | | ImageSize1 = 300 | ||
| + | | ImageAlt1 = | ||
| + | | ImageName1 = | ||
| + | | ImageCaption1 = Hair-like crystals of salicylic acid in the bottom of a beaker. (Click to see up close) | ||
| + | | ImageFile2 = Salicylic Acid structure.jpg | ||
| + | | ImageSize2 = 200 | ||
| + | | ImageAlt2 = | ||
| + | | ImageName2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFile3 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize3 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt3 = | ||
| + | | ImageName3 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR2 = | ||
| + | <!-- Sections --> | ||
| + | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | 3DMet = | ||
| + | | Abbreviations = | ||
| + | | SMILES = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| + | | AtmosphericOHRateConstant = | ||
| + | | Appearance = Colorless crystalline solid | ||
| + | | BoilingPt = | ||
| + | | BoilingPtC = 200 | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_notes = (decomposes) | ||
| + | | Density = 1.443 g/cm<sup>3</sup> (20 °C) | ||
| + | | Formula = C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>6</sub>O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | | HenryConstant = | ||
| + | | LogP = 2.26 | ||
| + | | MolarMass = 138.12 g/mol | ||
| + | | MeltingPt = | ||
| + | | MeltingPtC = 158.6 | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | Odor = Odorless | ||
| + | | pKa = 1 = 2.97 (25 °C)<br>2 = 13.82 (20 °C) | ||
| + | | pKb = | ||
| + | | Solubility = 0.124 g/100 ml (0 °C)<br>0.248 g/100 ml (25 °C)<br>0.414 g/100 ml (40 °C)<br>1.741 g/100 ml (75 °C)<br>7.779 g/100 ml (100 °C) | ||
| + | | SolubleOther = Soluble in [[acetone]], [[chloroform]], [[diethyl ether]], [[ethanol]], [[methanol]], [[propanol]], oil of turpentine<br>Slightly soluble in [[benzene]], [[carbon tetrachloride|CCl<sub>4</sub>]], [[toluene]] | ||
| + | | Solubility1 = 39.6 g/100 g (23 °C) | ||
| + | | Solvent1 = acetone | ||
| + | | Solubility2 = 0.46 g/100 g (11.7 °C)<br>0.775 g/100 g (25 °C)<br>0.991 g/100 g (30.5 °C)<br>2.38 g/100 g (49.4 °C)<br>4.4 g/100 g (64.2 °C) | ||
| + | | Solvent2 = benzene | ||
| + | | Solubility3 = 2.22 g/100 ml (25 °C)<br>2.31 g/100 ml (30.5 °C) | ||
| + | | Solvent3 = chloroform | ||
| + | | Solubility4 = 40.67 g/100 g (−3 °C)<br>62.48 g/100 g (21 °C) | ||
| + | | Solvent4 = methanol | ||
| + | | Solubility5 = 2.43 g/100 g (23 °C) | ||
| + | | Solvent5 = olive oil | ||
| + | | VaporPressure = 8.2·10<sup>-5</sup> mmHg (25 °C) | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | ||
| + | | Coordination = | ||
| + | | CrystalStruct = | ||
| + | | MolShape = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section4 = {{Chembox Thermochemistry | ||
| + | | DeltaGf = | ||
| + | | DeltaHc = 3,025 kJ/mol | ||
| + | | DeltaHf = -589.9 kJ/mol | ||
| + | | Entropy = | ||
| + | | HeatCapacity = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section5 = {{Chembox Explosive | ||
| + | | ShockSens = | ||
| + | | FrictionSens = | ||
| + | | DetonationV = | ||
| + | | REFactor = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section6 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| + | | AutoignitionPt = 540 °C (1,004 °F; 813 K) | ||
| + | | ExploLimits = | ||
| + | | ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/Ml2QPes/salicylic-acid-sa.pdf.html Sigma-Aldrich] | ||
| + | | FlashPt = 157 °C (315 °F; 430 K) (closed cup) | ||
| + | | LD50 = 480 mg/kg (mice, oral) | ||
| + | | LC50 = | ||
| + | | MainHazards = Irritant | ||
| + | | NFPA-F = | ||
| + | | NFPA-H = | ||
| + | | NFPA-R = | ||
| + | | NFPA-S = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section7 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| + | | OtherAnions = | ||
| + | | OtherCations = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction_label = | ||
| + | | OtherCompounds = [[Acetylsalicylic acid]]<br>[[Phenol]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
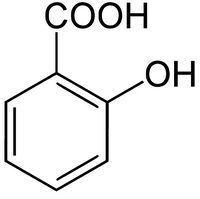
'''Salicylic acid''' is the organic compound with the chemical formula '''C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>4</sub>(OH)COOH'''. It is an example of a phenolic acid. It is the active metabolite of [[acetylsalicylic acid|aspirin]] and is also used in many other medications such as skin-care products. | '''Salicylic acid''' is the organic compound with the chemical formula '''C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>4</sub>(OH)COOH'''. It is an example of a phenolic acid. It is the active metabolite of [[acetylsalicylic acid|aspirin]] and is also used in many other medications such as skin-care products. | ||
| − | |||
== Properties == | == Properties == | ||
=== Chemical === | === Chemical === | ||
Salicylic acid can be converted to phenol via heating. | Salicylic acid can be converted to phenol via heating. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>4</sub>(OH)COOH → C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>OH + CO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Esterification with [[acetic anhydride]] gives aspirin. | ||
=== Physical === | === Physical === | ||
| − | Salicylic acid is most often encountered as a fine, fluffy crystalline powder or as needle-like crystals which are difficult to compact. It has a somewhat minty and irritating odor. Salicylic acid is quite soluble in alcohols, acetone, ether, and nonpolar solvents such as benzene and toluene, has low solubility in cold to warm water, and high solubility in boiling water. | + | Salicylic acid is most often encountered as a fine, fluffy crystalline powder or as needle-like crystals which are difficult to compact. It has a somewhat minty and irritating odor. Salicylic acid is quite soluble in alcohols, [[acetone]], ether, and slightly lower in nonpolar solvents, such as [[benzene]] and [[toluene]], has low solubility in cold to warm water, and high solubility in boiling water. |
| + | |||
| + | == Availability== | ||
| + | Salicylic acid, while usually produced using aspirin as a precursor with ease, can also be purchased in solution as various skin-care products for treating warts or acne, those these can be both expensive and impure, as well as highly diluted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It can also be found in food stores as preservative, usually as a ester or salt, or sometimes as free acid. Sodium salicylate is more commonly available. The obtain the free acid, simply add a stronger acid to the sodium salt and purify the compound. | ||
==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 140: | ||
Salicylic acid can be easily synthesized using either [[methyl salicylate]] or [[acetylsalicylic acid]] (aspirin) as the primary precursor, but because methyl salicylate may not be as cheaply or easily obtained as aspirin, it is usually synthesized from the latter, which is also typically seen as the easier process. | Salicylic acid can be easily synthesized using either [[methyl salicylate]] or [[acetylsalicylic acid]] (aspirin) as the primary precursor, but because methyl salicylate may not be as cheaply or easily obtained as aspirin, it is usually synthesized from the latter, which is also typically seen as the easier process. | ||
| − | Production from aspirin requires the acetylsalicylic acid to be refluxed in the presence of a stronger acid(often [[hydrochloric acid]]) for a period of time, hydrolyzing it to salicylic acid and [[acetic acid]]. The product can then be washed and recrystallized. | + | Production from aspirin requires the acetylsalicylic acid to be refluxed in the presence of a stronger acid (often [[hydrochloric acid]]) for a period of time, hydrolyzing it to salicylic acid and [[acetic acid]]. The product can then be washed and recrystallized. |
[[File:Sali1.jpg|thumb|268x268px|A reflux setup for producing salicylic acid by [[Synthesis of salicylic acid from methyl salicylate, by Alexleyenda|Alexleyenda's process]].]] | [[File:Sali1.jpg|thumb|268x268px|A reflux setup for producing salicylic acid by [[Synthesis of salicylic acid from methyl salicylate, by Alexleyenda|Alexleyenda's process]].]] | ||
Salicylic acid can also be prepared from store-bought oil of wintergreen ([[methyl salicylate]]); a detailed write-up for this process can be found [[Synthesis_of_salicylic_acid#alexleyenda.27s_synthesis_from_methyl_salicylate|here]]. | Salicylic acid can also be prepared from store-bought oil of wintergreen ([[methyl salicylate]]); a detailed write-up for this process can be found [[Synthesis_of_salicylic_acid#alexleyenda.27s_synthesis_from_methyl_salicylate|here]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Projects == | == Projects == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 151: | ||
* Reaction of salicylic acid with carbamide and boric acid to form Salicylamide | * Reaction of salicylic acid with carbamide and boric acid to form Salicylamide | ||
* Make [[phenol]] | * Make [[phenol]] | ||
| + | * Make Salsalate | ||
==Handling== | ==Handling== | ||
Revision as of 21:48, 18 June 2017
 Hair-like crystals of salicylic acid in the bottom of a beaker. (Click to see up close)
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Hydroxybenzoic acid
| |
| Other names
2-Carboxyphenol
O-Carboxyphenol O-hydroxybenzoic acid | |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 138.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.443 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 158.6 °C (317.5 °F; 431.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) (decomposes) |
| 0.124 g/100 ml (0 °C) 0.248 g/100 ml (25 °C) 0.414 g/100 ml (40 °C) 1.741 g/100 ml (75 °C) 7.779 g/100 ml (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, chloroform, diethyl ether, ethanol, methanol, propanol, oil of turpentine Slightly soluble in benzene, CCl4, toluene |
| Solubility in acetone | 39.6 g/100 g (23 °C) |
| Solubility in benzene | 0.46 g/100 g (11.7 °C) 0.775 g/100 g (25 °C) 0.991 g/100 g (30.5 °C) 2.38 g/100 g (49.4 °C) 4.4 g/100 g (64.2 °C) |
| Solubility in chloroform | 2.22 g/100 ml (25 °C) 2.31 g/100 ml (30.5 °C) |
| Solubility in methanol | 40.67 g/100 g (−3 °C) 62.48 g/100 g (21 °C) |
| Solubility in olive oil | 2.43 g/100 g (23 °C) |
| Vapor pressure | 8.2·10-5 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1 = 2.97 (25 °C) 2 = 13.82 (20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-589.9 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 157 °C (315 °F; 430 K) (closed cup) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
480 mg/kg (mice, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Acetylsalicylic acid Phenol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Salicylic acid is the organic compound with the chemical formula C6H4(OH)COOH. It is an example of a phenolic acid. It is the active metabolite of aspirin and is also used in many other medications such as skin-care products.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Salicylic acid can be converted to phenol via heating.
- C6H4(OH)COOH → C6H5OH + CO2
Esterification with acetic anhydride gives aspirin.
Physical
Salicylic acid is most often encountered as a fine, fluffy crystalline powder or as needle-like crystals which are difficult to compact. It has a somewhat minty and irritating odor. Salicylic acid is quite soluble in alcohols, acetone, ether, and slightly lower in nonpolar solvents, such as benzene and toluene, has low solubility in cold to warm water, and high solubility in boiling water.
Availability
Salicylic acid, while usually produced using aspirin as a precursor with ease, can also be purchased in solution as various skin-care products for treating warts or acne, those these can be both expensive and impure, as well as highly diluted.
It can also be found in food stores as preservative, usually as a ester or salt, or sometimes as free acid. Sodium salicylate is more commonly available. The obtain the free acid, simply add a stronger acid to the sodium salt and purify the compound.
Preparation
Salicylic acid can be easily synthesized using either methyl salicylate or acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) as the primary precursor, but because methyl salicylate may not be as cheaply or easily obtained as aspirin, it is usually synthesized from the latter, which is also typically seen as the easier process.
Production from aspirin requires the acetylsalicylic acid to be refluxed in the presence of a stronger acid (often hydrochloric acid) for a period of time, hydrolyzing it to salicylic acid and acetic acid. The product can then be washed and recrystallized.

Salicylic acid can also be prepared from store-bought oil of wintergreen (methyl salicylate); a detailed write-up for this process can be found here.
Projects
- Make aspirin
- Esterification of salicylic acid with methanol to make methyl salicylate
- Reaction of salicylic acid with carbamide and boric acid to form Salicylamide
- Make phenol
- Make Salsalate
Handling
Safety
Salicylic acid has the ability to break down lipids in the skin, causing symptoms ranging from dryness and irritation at low concentrations to mild acid burns at higher ones. When ingested orally in large amounts it can cause salicylate intoxication, which may produce very serious side effects.
Storage
No special storage is require, salicylic acid can be stored in any clean container.
Disposal
Salicylic acid can be safely poured down the drain, as it does not pose any danger for the environment.
