Difference between revisions of "Barbituric acid"
(→Relevant Sciencemadness threads) |
|||
| Line 158: | Line 158: | ||
[[Category:Acids]] | [[Category:Acids]] | ||
[[Category:Weak acids]] | [[Category:Weak acids]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Solids]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:03, 1 March 2021
 Barbituric acid on a watchglass
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
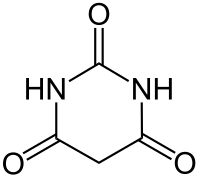
| IUPAC name
Pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione
| |||
| Other names
1,3-Diazinane-2,4,6-trione; 2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione; 2,4,6-Trioxohexahydropyrimidine; 2,4,6-Trihydroxypyrimidine; 2,4,6-Trioxypyrimidine; 2,4,6-Pyrimidinetriol; 2,4,6-Pyrimidinetrione; 2,4,6-Trihydroxy-1,3-diazine; 6-Hydroxy-hydrouracil; 6-Hydroxyuracil; Malonylurea; Pyrimidinetriol; N,N-(1,3-dioxo-1,3-propanediyl)urea; N,N-Malonylurea
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4N2O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 128.09 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Odor | Slight | ||
| Melting point | 245 °C (473 °F; 518 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 260 °C (500 °F; 533 K) (decomposes) | ||
| 14.2 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in formaldehyde 37%, conc. formic acid Slightly soluble in pyridine Almost insoluble in HCl 37% Insoluble in glacial acetic acid, acetone, acetonitrile, alcohols, ammonia 25%, chloroform, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, heptane, hexane, methyl acetate, toluene, xylene | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
5,000 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Barbituric acid or malonylurea is an organic compound based on a pyrimidine heterocyclic skeleton. Barbituric acid is the parent compound of barbiturate drugs, although barbituric acid itself is not pharmacologically active.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Barbituric acid will react with a hot aq. solution of sodium nitrite to form sodium violurate.[1]
Barbituric acid will form a colored complex with pyridine and cyanide ions. This reaction is used in the detection of cyanides.
Physical
Barbituric acid is a white solid, moderately soluble in water and insoluble in most organic solvents, but shows good solubility in aq. formaldehyde and conc. formic acid. Solutions of barbituric acid will oxidize in air, turning yellow then brownish after several hours and days. It has a weak odor.
Availability
Barbituric acid is sold by chemical suppliers, however it is classified as controlled substance in most countries, making it near impossible for the amateur chemist to acquire it freely.
Preparation
Barbituric acid can be synthesized from the reaction of malonic acid, urea and phosphoryl chloride. For better yields, diethyl malonate can be used instead of malonic acid. Chemplayer obtained slightly oxidized barbituric acid from diethyl malonate and urea, with sodium ethoxide being as a condensing agent.
Another way to synthesize barbituric acid can be prepared by reducing 5,5-dibromobarbituric acid with HCN or sodium amalgam and hydrogen iodide.
Projects
- Make vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
- Make pyridine/barbituric acid reagent (cyanide detection)
- Make violuric acid
Handling
Safety
Barbituric acid should be handled with care and proper protection.
Overdose of barbituric acid can cause respiratory problems and death. Barbituric acid derivatives are considered DEA Schedule III controlled substances.
Storage
Solid barbituric acid should be kept in closed bottles. Solutions of barbituric acid are stable for a day before darkening, and can be safely used up to a week.
Disposal
Barbituric acid can be poured down the drain, though it's advised to neutralize it first, using an oxidizing mixture if possible.