Difference between revisions of "Nonane"
(Added image.) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Chembox | {{Chembox | ||
| − | | Name =Nonane | + | | Name = Nonane |
| Reference = | | Reference = | ||
| − | | IUPACName =n- | + | | IUPACName = n-Nonane |
| PIN = | | PIN = | ||
| − | | SystematicName =Nonane | + | | SystematicName = Nonane |
| − | | OtherNames = | + | | OtherNames = |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<!-- Images --> | <!-- Images --> | ||
| − | | ImageFile = | + | | ImageFile = Nonane structural formula.png |
| ImageSize = | | ImageSize = | ||
| ImageAlt = | | ImageAlt = | ||
| Line 54: | Line 49: | ||
| Appearance = Colorless viscous liquid | | Appearance = Colorless viscous liquid | ||
| BoilingPt = | | BoilingPt = | ||
| − | | BoilingPtC = | + | | BoilingPtC = 150.4-151.0 |
| BoilingPt_ref = | | BoilingPt_ref = | ||
| − | | BoilingPt_notes = | + | | BoilingPt_notes = |
| Density = 0.718 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | | Density = 0.718 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| Formula = C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>20</sub> | | Formula = C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>20</sub> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 58: | ||
| MolarMass = 128.26 g/mol | | MolarMass = 128.26 g/mol | ||
| MeltingPt = | | MeltingPt = | ||
| − | | MeltingPtC = | + | | MeltingPtC = −54.1 - −53.1 |
| MeltingPt_ref = | | MeltingPt_ref = | ||
| − | | MeltingPt_notes = | + | | MeltingPt_notes = |
| Odor = Gasoline-like | | Odor = Gasoline-like | ||
| pKa = | | pKa = | ||
| pKb = | | pKb = | ||
| Solubility = Insoluble | | Solubility = Insoluble | ||
| − | | SolubleOther = | + | | SolubleOther = Miscible with hydrocarbons, halocarbons |
| Solvent = | | Solvent = | ||
| VaporPressure = 0.59 kPa (at 25.0 °C) | | VaporPressure = 0.59 kPa (at 25.0 °C) | ||
| Line 118: | Line 113: | ||
===Chemical=== | ===Chemical=== | ||
Nonane will burn in air in the presence of an ignition source. | Nonane will burn in air in the presence of an ignition source. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>20</sub> + 14 O<sub>2</sub> → 9 CO<sub>2</sub> + 10 H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
===Physical=== | ===Physical=== | ||
| Line 128: | Line 125: | ||
==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| + | One way of obtaining (relative) pure nonane is through the decarboxylation of capric acid and its salts. However, this process will also give many side products and purification is required. | ||
| + | |||
Nonane is best purchased than prepared. | Nonane is best purchased than prepared. | ||
| Line 150: | Line 149: | ||
[[Category:Chemical compounds]] | [[Category:Chemical compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Organic compounds]] | [[Category:Organic compounds]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Hydrocarbons]] | ||
[[Category:Alkanes]] | [[Category:Alkanes]] | ||
[[Category:Solvents]] | [[Category:Solvents]] | ||
[[Category:Nonpolar solvents]] | [[Category:Nonpolar solvents]] | ||
[[Category:Liquids]] | [[Category:Liquids]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:33, 24 September 2020
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
n-Nonane
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Nonane | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H20 | |
| Molar mass | 128.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless viscous liquid |
| Odor | Gasoline-like |
| Density | 0.718 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −54.1 – −53.1 °C (−65.4 – −63.6 °F; 219.1–220.1 K) |
| Boiling point | 150.4–151.0 °C (302.7–303.8 °F; 423.5–424.1 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Miscible with hydrocarbons, halocarbons |
| Vapor pressure | 0.59 kPa (at 25.0 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−275.7 – −273.7 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ScienceLab |
| Flash point | 31.0 °C |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Octane Decane |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
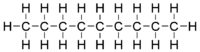
Nonane or n-nonane is an organic chemical compound, a straight-chain hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20. Unlike most alkanes, the numeric prefix in its name derives from Latin, rather than Greek (using a Greek prefix would be enneane).
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Nonane will burn in air in the presence of an ignition source.
- C9H20 + 14 O2 → 9 CO2 + 10 H2O
Physical
Nonane is a colorless liquid, with a petroleum odor, insoluble in water, but miscible with other organic solvents.
Availability
Nonane can be extracted from various petroleum solvents, such as Stoddard solvent (which contains a mixture of aliphatic and alicyclic C7 to C12 hydrocarbons), via fractional distillation, though you need a large amount of Stoddard solvent to obtain any useful amount of n-nonane.
Nonane can also be purchased from chemical suppliers.
Preparation
One way of obtaining (relative) pure nonane is through the decarboxylation of capric acid and its salts. However, this process will also give many side products and purification is required.
Nonane is best purchased than prepared.
Projects
- Organic extractions
Handling
Safety
Nonane vapors are irritant and because it's flammable, it is considered a fire hazard. However, as it is less volatile than most alkanes, its vapors are generally less of a problem.
Storage
In closed bottles, away from any heat source.
Disposal
Nonane can be safely burned.
References
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
No threads so far. Why not start one?
- Chemical pages without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Organic compounds
- Hydrocarbons
- Alkanes
- Solvents
- Nonpolar solvents
- Liquids