Difference between revisions of "FOX-7"
(→Preparation) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| OtherNames = 1,1-Diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene<br>DADNE<br>FOX7 | | OtherNames = 1,1-Diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene<br>DADNE<br>FOX7 | ||
<!-- Images --> | <!-- Images --> | ||
| − | | ImageFile = | + | | ImageFile = FOX-7 structure.png |
| − | | ImageSize = | + | | ImageSize = 200 |
| ImageAlt = | | ImageAlt = | ||
| ImageName = | | ImageName = | ||
| + | | ImageCaption = Structure of FOX-7 | ||
| ImageFile1 = | | ImageFile1 = | ||
| ImageSize1 = | | ImageSize1 = | ||
| Line 134: | Line 135: | ||
==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| + | There are several synthesis routes described in literature. | ||
| + | |||
One synthesis of FOX-7 involves nitrating 2-methylimidazole, using concentrated [[nitric acid]] and concentrated [[sulfuric acid]] (80-100%), which gives parabanic acid and 2-dinitromethylene-4,4-dinitroimidazolidin-5-one. If [[oleum]] is used instead, the latter compound is not formed, instead parabanic acid and 2-methyl-4-nitroimidazole are formed. Thus oleum cannot be used for nitration. The resulting 2-dinitromethylene-4,4-dinitroimidazolidin-5-one precipitates out of the reaction and is filtered off. Thi compound is unstable at room temperature, and decomposes to 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione releasing [[dinitrogen trioxide]]. The resulting 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione is subsequently hydrolyzed with aqueous [[ammonia]] to give FOX-7 and oxalate. The resulting product is purified and dried. Yield is given as 15%.<ref>Latypov NV, Bergman J, Langlet A, Wellmar U, Bemm U (1998) Tetrahedron 54:11525</ref><ref>https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783540722014</ref> | One synthesis of FOX-7 involves nitrating 2-methylimidazole, using concentrated [[nitric acid]] and concentrated [[sulfuric acid]] (80-100%), which gives parabanic acid and 2-dinitromethylene-4,4-dinitroimidazolidin-5-one. If [[oleum]] is used instead, the latter compound is not formed, instead parabanic acid and 2-methyl-4-nitroimidazole are formed. Thus oleum cannot be used for nitration. The resulting 2-dinitromethylene-4,4-dinitroimidazolidin-5-one precipitates out of the reaction and is filtered off. Thi compound is unstable at room temperature, and decomposes to 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione releasing [[dinitrogen trioxide]]. The resulting 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione is subsequently hydrolyzed with aqueous [[ammonia]] to give FOX-7 and oxalate. The resulting product is purified and dried. Yield is given as 15%.<ref>Latypov NV, Bergman J, Langlet A, Wellmar U, Bemm U (1998) Tetrahedron 54:11525</ref><ref>https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783540722014</ref> | ||
| − | A second route involves the following: Acetamidine hydrochloride and diethyl oxalate react with a solution of [[sodium methoxide]] in anhydrous [[methanol]], producing the methanol adduct of 2-methylimidazolidine-4,5-dione, which is | + | A second route involves the following: [[Acetamidine hydrochloride]] and diethyl oxalate react with a solution of [[sodium methoxide]] in anhydrous [[methanol]], producing the methanol adduct of 2-methylimidazolidine-4,5-dione, which is recrystallized from dry methanol. The purified product is nitrated with a [[nitrating mixture]] below 30 °C to 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione (yield: 67%), which, on hydrolysis with aqueous ammonia, will give FOX-7 (yield: 87%; 37% overall from acetamidine hydrochloride).<ref>Latypov NV, Bergman J, Langlet A, Wellmar U, Bemm U (1998) Tetrahedron 54:11525</ref><ref>https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0304389406002251</ref> |
A third route is given as: Acetamidine hydrochloride and diethyl malonate react in a solution of [[sodium ethoxide]] in anhydrous [[ethanol]] produces 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine which is nitrated using a nitrating mixture at low temperature to 2-dinitromethyleme-5,5-dinitrodihydropyrimidine-4,6-dione which is easily hydrolyzed in water to FOX-7 and [[dinitromethane]]. This reaction has the advantage of also producing dinitromethane, which is a useful compound that is somewhat hard to obtain, though in large scale it's difficult to purify and its presence may affect the final purity of FOX-7. The main advantage of this route is that 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine is easier to isolate and purify than 2-methylimidazolidine-4,5-dione.<ref>https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0304389406002251</ref> | A third route is given as: Acetamidine hydrochloride and diethyl malonate react in a solution of [[sodium ethoxide]] in anhydrous [[ethanol]] produces 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine which is nitrated using a nitrating mixture at low temperature to 2-dinitromethyleme-5,5-dinitrodihydropyrimidine-4,6-dione which is easily hydrolyzed in water to FOX-7 and [[dinitromethane]]. This reaction has the advantage of also producing dinitromethane, which is a useful compound that is somewhat hard to obtain, though in large scale it's difficult to purify and its presence may affect the final purity of FOX-7. The main advantage of this route is that 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine is easier to isolate and purify than 2-methylimidazolidine-4,5-dione.<ref>https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0304389406002251</ref> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:49, 28 December 2020
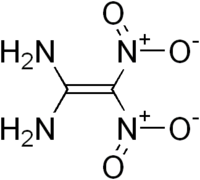 Structure of FOX-7
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2-Dinitroethene-1,1-diamine
| |
| Other names
1,1-Diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene
DADNE FOX7 | |
| Properties | |
| C2H4N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 148.08 g/mol |
| Appearance | Bright yellow crystalline powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.885 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 238 °C (460 °F; 511 K) (decomposes) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Poorly soluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMF, DMSO, NMP |
| Vapor pressure | ~0 mmHg |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
–130 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | None |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
TATB |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
FOX-7 or 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethene (DADNE) is an insensitive high explosive compound, which has been shown to have better properties than classical high explosive materials, such as TNT and RDX.[1]
Contents
Properties
Chemical
When heated with in an aq. sol. of potassium hydroxide, the potassium salt of dinitromethane is produced.
Addition of guanidinium chloride to FOX-7 in an aq. solution of KOH will give the guanidinium salt of FOX-7.
FOX-7 will burn if ignited, but will only detonate if initiated by a blasting cap.
Physical
FOX-7 is a bright yellow crystalline powder, poorly soluble in water and most organic solvents, though it shows good solubility in dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone.[2]
Recrystallization is possible from dilute hydrochloric acid, γ-butyrolactone or water with the acid being the most efficient solvent. FOX-7 may also be recrystallised from DMF or NMP (and presumably DMSO) by dissolving the FOX-7 in the respective solvent at 70 °C and then adding 4–5 equivalents of hot ethanol, methanol or water to precipitate FOX-7. The product from this method of recrystallization is reported to have improved sensitiveness properties compared with unpurified FOX-7.[3]
Explosive
FOX-7 is considered a very powerful yet very stable explosive compound. It has low friction and shock sensitivity and does not detonate upon exposure to heat or open flame. The impact sensitivity of recrystallised FOX-7 to be 126 - 159 cm compared with 38 cm for RDX in the 2 kg BAM dropweight apparatus. Its detonation velocity has been estimated to be 8,870 m/s at a crystal density 1.885 g/cm3, while a measured value of 8,335 m/s has been obtained at a density of 1.756 g/cm3.
The detonation velocity of mixtures containing 80% FOX-7 with binders is comparable to Composition B (60/40 RDX/TNT with 1% paraffin wax) and nearly pure FOX-7 based plastic bonded explosives are slightly superior to RDX, though it's far less sensitive than RDX.
Both FOX-7 and RDX have the same oxygen balance (–21.6%) due to having the same element ratio.
Availability
FOX-7 is not available commercially and has to be made it situ.
Preparation
There are several synthesis routes described in literature.
One synthesis of FOX-7 involves nitrating 2-methylimidazole, using concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid (80-100%), which gives parabanic acid and 2-dinitromethylene-4,4-dinitroimidazolidin-5-one. If oleum is used instead, the latter compound is not formed, instead parabanic acid and 2-methyl-4-nitroimidazole are formed. Thus oleum cannot be used for nitration. The resulting 2-dinitromethylene-4,4-dinitroimidazolidin-5-one precipitates out of the reaction and is filtered off. Thi compound is unstable at room temperature, and decomposes to 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione releasing dinitrogen trioxide. The resulting 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione is subsequently hydrolyzed with aqueous ammonia to give FOX-7 and oxalate. The resulting product is purified and dried. Yield is given as 15%.[4][5]
A second route involves the following: Acetamidine hydrochloride and diethyl oxalate react with a solution of sodium methoxide in anhydrous methanol, producing the methanol adduct of 2-methylimidazolidine-4,5-dione, which is recrystallized from dry methanol. The purified product is nitrated with a nitrating mixture below 30 °C to 2-dinitromethyleneimidazolidine-4,5-dione (yield: 67%), which, on hydrolysis with aqueous ammonia, will give FOX-7 (yield: 87%; 37% overall from acetamidine hydrochloride).[6][7]
A third route is given as: Acetamidine hydrochloride and diethyl malonate react in a solution of sodium ethoxide in anhydrous ethanol produces 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine which is nitrated using a nitrating mixture at low temperature to 2-dinitromethyleme-5,5-dinitrodihydropyrimidine-4,6-dione which is easily hydrolyzed in water to FOX-7 and dinitromethane. This reaction has the advantage of also producing dinitromethane, which is a useful compound that is somewhat hard to obtain, though in large scale it's difficult to purify and its presence may affect the final purity of FOX-7. The main advantage of this route is that 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine is easier to isolate and purify than 2-methylimidazolidine-4,5-dione.[8]
Projects
- Make blasting charges
Handling
Safety
FOX-7 is a powerful explosive and like all nitro compounds it must be handled with care.
Storage
In closed bottles.
Disposal
Controlled incineration should suffice.
References
- ↑ http://www.wydawnictwa.ipo.waw.pl/cejem/Vol-13-Number-2-2016/Trzcinski.pdf
- ↑ Anniyappan M., Talawar M.B., Gore G.M., Venugopalan S., Ganghe B.R., Synthesis, Characterization and Thermolysis of 1,1-Diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7) and Its Salts, J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, B137, 812-819
- ↑ Bergman, H., Personal Communication, (2001), 28 March 2001
- ↑ Latypov NV, Bergman J, Langlet A, Wellmar U, Bemm U (1998) Tetrahedron 54:11525
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783540722014
- ↑ Latypov NV, Bergman J, Langlet A, Wellmar U, Bemm U (1998) Tetrahedron 54:11525
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0304389406002251
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0304389406002251