Difference between revisions of "Einsteinium"
From Sciencemadness Wiki
(Added categories.) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
<!-- Periodic table --> | <!-- Periodic table --> | ||
|above= [[Holmium|Ho]] | |above= [[Holmium|Ho]] | ||
| − | |below= | + | |below= Upt |
|left= [[Californium]] | |left= [[Californium]] | ||
|right= [[Fermium]] | |right= [[Fermium]] | ||
| Line 271: | Line 271: | ||
|engvar= | |engvar= | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Einsteinium is an extremely radioactive element. It's very close to impossible to obtain this element in a hobby or even a professional laboratory. | + | '''Einsteinium''' ('''Es''') is an extremely radioactive element. It's very close to impossible to obtain this element in a hobby or even a professional laboratory. |
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
===Chemical=== | ===Chemical=== | ||
| − | + | Little is known about this element's chemical properties. | |
===Physical=== | ===Physical=== | ||
| − | + | It is a highly radioactive element. | |
==Availability== | ==Availability== | ||
| Line 290: | Line 290: | ||
==Handling== | ==Handling== | ||
| − | |||
===Safety=== | ===Safety=== | ||
Einsteinium is extremely radioactive. Any sort of contact or exposition will more likely than not lead to radiation poisoning. | Einsteinium is extremely radioactive. Any sort of contact or exposition will more likely than not lead to radiation poisoning. | ||
| + | |||
===Storage=== | ===Storage=== | ||
Store in a thick lead container. | Store in a thick lead container. | ||
| + | |||
===Disposal=== | ===Disposal=== | ||
To do | To do | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
===Relevant Sciencemadness threads=== | ===Relevant Sciencemadness threads=== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Category:Elements]] | [[Category:Elements]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Metals]] | ||
| + | [[Category:F-block]] | ||
[[Category:Radioactives]] | [[Category:Radioactives]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:28, 11 October 2022
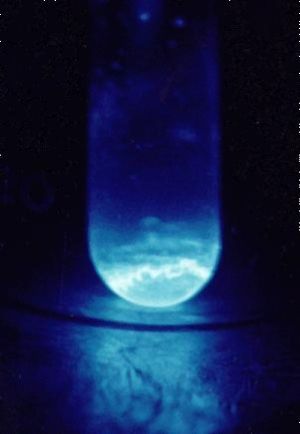 A 300 microgram sample of Einsteinium, glowing in the dark. | |||||
| General properties | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name, symbol | Einsteinium, Es | ||||
| Appearance | Metallic. Glows blue in the dark. | ||||
| Einsteinium in the periodic table | |||||
| |||||
| Atomic number | 99 | ||||
| Standard atomic weight (Ar) | |||||
| Group, block | n/a; f-block | ||||
| Period | period 7 | ||||
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f11 7s2 | ||||
per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 29, 8, 2 | ||||
| Physical properties | |||||
| Phase | Solid | ||||
| Melting point | 1133 K (860 °C, 1580 °F) | ||||
| Boiling point | 1269 K (996 °C, 1825 °F) (Estimated) | ||||
| Density near r.t. | 8.84 g/cm3 | ||||
| Atomic properties | |||||
| Oxidation states | +2, +3, +4 | ||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.3 | ||||
| energies | 1st: 619 kJ/mol | ||||
| Miscellanea | |||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | ||||
| CAS Registry Number | 7429-92-7 | ||||
| History | |||||
| Discovery | Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (1952) | ||||
| Named by | after Albert Einstein | ||||
Einsteinium (Es) is an extremely radioactive element. It's very close to impossible to obtain this element in a hobby or even a professional laboratory.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Little is known about this element's chemical properties.
Physical
It is a highly radioactive element.
Availability
To do
Isolation
To do
Projects
- Element collection
Handling
Safety
Einsteinium is extremely radioactive. Any sort of contact or exposition will more likely than not lead to radiation poisoning.
Storage
Store in a thick lead container.
Disposal
To do