Difference between revisions of "Benzophenone"
m (→Preparation) |
(→Preparation) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
| AutoignitionPt = 650 °C (1202 °F; 923 K) | | AutoignitionPt = 650 °C (1202 °F; 923 K) | ||
| ExploLimits = | | ExploLimits = | ||
| − | | ExternalMSDS = [] | + | | ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/VIyOKRE/benzophenone-sa.pdf Sigma-Aldrich] |
| FlashPt = 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) | | FlashPt = 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) | ||
| LD50 = | | LD50 = | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
'''Benzophenone''' is the simplest di-[[aryl]] [[ketone]]. | '''Benzophenone''' is the simplest di-[[aryl]] [[ketone]]. | ||
| − | It is often used in [[drying solvents]] together with [[sodium]] metal. | + | It is often used in [[drying solvents]] together with [[sodium]] metal, to produce a very dry solvent suitable for Grignard reagents. |
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
| Line 121: | Line 120: | ||
Benzophenone can be reduced by [[sodium]] metal to produce the intensely blue colored benzophenone ketyl radical. This is highly reactive towards [[water]] and [[oxygen]] so it can be used as an indicator of solvent dryness. | Benzophenone can be reduced by [[sodium]] metal to produce the intensely blue colored benzophenone ketyl radical. This is highly reactive towards [[water]] and [[oxygen]] so it can be used as an indicator of solvent dryness. | ||
| − | Benzophenone is a strong UV absorber, owing to cross-conjugation. This results in its use as a UV photoinitiator in some UV curing resins. Derivatives of benzophenone are often used in sunscreens and as an additive to prevent the UV-induced degradation of polymers. | + | Benzophenone is a strong UV absorber, owing to cross-conjugation. This results in its use as a UV photoinitiator in some UV curing resins. Derivatives of benzophenone are often used in sunscreens and as an additive to prevent the UV-induced degradation of polymers and other organic compounds. |
===Physical=== | ===Physical=== | ||
| Line 132: | Line 131: | ||
Benzophenone is produced by the [[copper]]-catalyzed oxidation of diphenylmethane with oxygen from air. | Benzophenone is produced by the [[copper]]-catalyzed oxidation of diphenylmethane with oxygen from air. | ||
| − | It can also be produced by the ketonic decarboxylation of calcium benzoate. | + | It can also be produced by the ketonic decarboxylation of calcium benzoate<ref>https://www.prepchem.com/synthesis-of-benzophenone/</ref>. |
==Projects== | ==Projects== | ||
*Photosensitizer in photochemistry | *Photosensitizer in photochemistry | ||
*Water indicator in air-free techniques | *Water indicator in air-free techniques | ||
| + | *Synthesis of [[diphenylmethanol]] | ||
==Handling== | ==Handling== | ||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
*[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=11208 benzophenone synthesis] | *[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=11208 benzophenone synthesis] | ||
*[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=20540 Lewis acid for benzophenone synthesis with benzoyl bromide] | *[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=20540 Lewis acid for benzophenone synthesis with benzoyl bromide] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Chemical compounds]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Organic compounds]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Aromatic compounds]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Ketones]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Solids]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:13, 9 July 2022
 |
This article is a stub. Please help Sciencemadness Wiki by expanding it, adding pictures, and improving existing text.
|
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
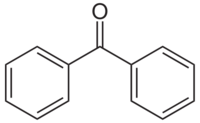
Diphenylmethanone
| |
| Other names
Benzophenone
Diphenyl ketone Benzoylbenzene Benzoylphenyl Diphenylmethanone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 119-61-9 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10O | |
| Molar mass | 182.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Odor | Geranium-like |
| Density | 1.11 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 48.5 °C (119.3 °F; 321.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 305.4 °C (581.7 °F; 578.5 K) |
| 0.0137 g/100 ml (at 25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Soluble in glacial acetic acid, acetone, benzene, carbon disulfide, CCl4, methanol |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | 16.6 g/100 ml |
| Solubility in ethanol | 13.3 g/100 ml |
| Vapor pressure | 1.93·10-3 mm Hg at 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Acetophenone |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Benzophenone is the simplest di-aryl ketone.
It is often used in drying solvents together with sodium metal, to produce a very dry solvent suitable for Grignard reagents.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Benzophenone can be reduced by sodium metal to produce the intensely blue colored benzophenone ketyl radical. This is highly reactive towards water and oxygen so it can be used as an indicator of solvent dryness.
Benzophenone is a strong UV absorber, owing to cross-conjugation. This results in its use as a UV photoinitiator in some UV curing resins. Derivatives of benzophenone are often used in sunscreens and as an additive to prevent the UV-induced degradation of polymers and other organic compounds.
Physical
Benzophenone is a white solid, with a characteristic smell, practically insoluble in water, but more soluble in organic solvents.
Availability
Benzophenone is sold by lab suppliers. Can also be purchased from eBay.
Preparation
Benzophenone is produced by the copper-catalyzed oxidation of diphenylmethane with oxygen from air.
It can also be produced by the ketonic decarboxylation of calcium benzoate[1].
Projects
- Photosensitizer in photochemistry
- Water indicator in air-free techniques
- Synthesis of diphenylmethanol
Handling
Safety
Benzophenone is considered safe, but it may be irritant.
Storage
In sealed bottles.
Disposal
Can be neutralized by oxidizing it with an oxidizing solution/mixture.
References
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
- Article stubs
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Organic compounds
- Aromatic compounds
- Ketones
- Solids