| Pages:
1
2
3 |
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
You need spearmint oil, not peppermint oil. Peppermint oil lacks the necessary carvone that catalyzes the decarboxylation. I don't think DMF has
quite a high enough boiling point, and in any case, it's an amide, like proteins are. That means that you could have transamidation reactions with
your amino acid (theoretically), giving the formamide derivatives of your amino acids as well as dimethylamine. So the dimethylamine could be what
you're smelling.
The only amino acid I have significant amounts of now is proline, so I tried solventless decarboxylation with that. Of course, the decarboxylized
derivative of proline, (pyrollidine) has a boiling point that's like 90C, so it boils as soon as it forms. I should probably set up a distillation
rig and see what I can get from that.
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
LD5050
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 182
Registered: 16-1-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Melgar  | You need spearmint oil, not peppermint oil. Peppermint oil lacks the necessary carvone that catalyzes the decarboxylation. I don't think DMF has
quite a high enough boiling point, and in any case, it's an amide, like proteins are. That means that you could have transamidation reactions with
your amino acid (theoretically), giving the formamide derivatives of your amino acids as well as dimethylamine. So the dimethylamine could be what
you're smelling.
The only amino acid I have significant amounts of now is proline, so I tried solventless decarboxylation with that. Of course, the decarboxylized
derivative of proline, (pyrollidine) has a boiling point that's like 90C, so it boils as soon as it forms. I should probably set up a distillation
rig and see what I can get from that. |
The paper I read used d-pulegone (I'll have to find it and attach it) it was a paper on the impurities formed using different OTC solvents and
catylists. Surprisingly if I remember right turpintine and d-pulegone had pretty good yields around 75% if I recall correctly. I know the proper
catylist to use is spearmint oil but the only reason I used peppermint is because it's all I could find near me and well I found a document stating it
worked so what the hell I gave it a shot.
What temp does the tryptophan decarboxylate at? I was looking on google earlier but couldn't find the answer although I got interrupted 5 minutes into
the search so I'll try again to find it myself if I don't get an answer in the mean time.
So is my experiment pointless because DMF is an amide? Should I pretty much just stop what I'm doing because I'm not going to get anywhere lol. Ohhh
well it was worth a shot anyway I guess.
Also is a catylist necessary for decarboxylation or does it just speed up the reaction?
|
|
|
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
I've found that the catalyst is very much needed. If the catalyst ever boiled away on me, I'd get a lot of bumping, to the point where one vessel
actually fell off my hotplate. I had to keep a close watch for that.
You can use really any high-boiling solvent, or even no solvent, assuming the amine boils at a high enough temperature to act as a solvent. (And if
not, distill it as it forms.) Decarboxylation requires around 150C or so, but it could be higher or lower I'm sure, depending on the amino acid,
amount of catalyst, solvent, etc.
Pulegone does have the enone functionality that makes a catalyst effective, however peppermint oil has little if any pulegone in it. Carvone, on the
other hand, is the major component of spearmint oil.
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
Kratom3million
Harmless

Posts: 13
Registered: 3-10-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I have a question- is there any way you can decarboxylate phenylalanine to Phenethylamine (you can do it, google it erowid has a method) without heat?
My problem is I have a kitchen set up and I would like to produce pea from dl-phenylalanine but without having to cook (for the co2 release part)
because if it accidentally burnt me and my family would be ingesting fumes from grams of burnt phenylalanine. Example: you can produce hydrogen in a
cup of water with salt and a 9v battery. Is there any ways to do this type of thing but for co2 release? Thank you!!!
|
|
|
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
Why not just do it on a very small scale with an alcohol lamp and a test tube? There's really no getting around the fact that you're going to need to
use heat if you're going to do any real chemistry at all, ever. Alcohol lamps are easy to make, too. Just get a small bottle (nail polish bottles
work well) and then find some cotton cord that will fit inside the neck without falling in. You can use 70% isopropanol as a fuel. 70% doesn't
produce soot either, like 99% isopropanol does. Or use methanol, propylene glycol, or some other substance that burns and mixes with water. It
sounds like you might be a bit inexperienced, but if you use alcohol with water mixed in as your fuel, it's very easy to extinguish, even if you spill
the fuel all over yourself. (Though, try NOT to do that, obviously) The more water you add, the less flammable it is, so add an amount where it's a
bit difficult to light, but will burn once you light it. If you can't find cotton cord for a wick, then unroll a cotton ball and twist it into a
wick, or just twist a piece of paper towel tightly and cut it to an appropriate length.
Also, don't use your hands to hold the test tube, because it will get hotter than boiling water. Order like $5 worth of these things, you won't
regret it:
http://www.ebay.com/itm/Clamp-Heating-Glass-Tube-Tongs-Suppl...
In the meantime, you can rig something up with bent coat hanger wire or whatever you have around, I'm sure.
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
gatosgr
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 237
Registered: 7-4-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
If you don't have tongs , fold a strip of A4 print paper many times and use this long strip to cover the test tube, squeeze the paper to lift the
tube, don't touch the tube only the paper.
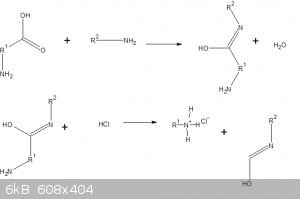
What is the mechanism for this reaction?
If the amino acid smells like rotten fish it's giving off di or trimethylamine.
[Edited on 13-10-2017 by gatosgr]
|
|
|
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
I hadn't experimented as much with tryptophan earlier, because it's one of the more expensive amino acids and I didn't have very much of it. I tried
again today though, in a 50 mL flask, after adding a stopper to it, and putting a glass tube sticking out of the top. I made the end that was in the
stopper taper to a narrow size, then put a bulge in the tube higher up. The effectively prevented the gushing problem I had earlier. I also added it
in portions, which was a little annoying, because I had to wait for it to cool down every time I wanted to add another portion. I also added silicone
oil to reduce the foaming. It certainly helped, but there was still a lot of foaming anyway. Anyway, after all these modifications, I was able to
decarboxylate tryptophan solventless with little if any visible oxidation, using spearmint oil as a catalyst. Tryptamine is an amorphous orange solid
at room temperature, and doesn't seem to have a fixed melting point; it just softens and becomes less viscous as it's heated. I'm not sure what else
I could have, and it certainly smells like tryptamine, but I'm not exactly sure how to test it. TLC, I guess?
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
gatosgr
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 237
Registered: 7-4-2015
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
What is the mechanism of the reaction?
[Edited on 28-10-2017 by gatosgr]
|
|
|
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
Enone-catalyzed decarboxylation of alpha amino acids. It was first reported in 1986:
https://erowid.org/archive/rhodium/chemistry/trp.decarbox.en...
Carvone occurs as the principle component of spearmint oil, and thus can act in a role similar to cyclohexenone.
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
spookyboo13
Harmless

Posts: 4
Registered: 3-1-2018
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Melgar,
Thanks for the heads up on spearmint oil. I quickly recognized the correlation between carvone the main active in spearmint oil and the formation of a
schiffs base between carvone and phenylalanine. In case your might not be aware the bright orange color your describing is the schiffs base itself,
as they are always brightly colored, lemony yellow to orange to brilliant red. With 30 plus years as an organic chemist in the fragrance industry, I
have produced dozens of them. Also when the schiffs base, also known as an imine, forms there is an instant generation of a large amount of heat and
in general water vapor sweats off. These are telltale signs that the complex is forming. Some schiffs bases don't form so easy and have to be heated
to initiate the formation of the complex. Just learn to recognize the bright colors, even in solution. Many schiffs bases can be formed neat,
especially if one component is a liquid you can just dissolve one in the other, heating if necessary. Normally the reaction generates so much heat you
wont be able to hold the flask! If both are solids dissolve them in a polar protic high boiling solvent like ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol or
propylene glycol. Amino acid Schiffs bases generally decarboxylate between 110 C and 190 C so just heat the hell out of it untill you get yet another
color change and evolution of CO2 gas. If your not sure just trap the gas over water and put a lit match in the receiving vessel, naturally CO2 will
extinguish the flame. Some amino acid schiffs bases require 2 or more hours to completely decarboxylate.
So here is my first set of runs:
8.25 grams of phenylalanine (free form) and 6.0 grams of phenylacetaldehyde and 10 grams of ethylene glycol were intimately mixed without heating at
which time a vigorous reaction set in generating an immense amount of heat and immediately turning a bright lemon-yellow color. After the initial heat
flash subsided the mixture was heated over a low flame to drive the formation to completion by this time the solution was a vivid orange color with a
beautiful floral-grape odor. heating was continued to bring the solution to a low boil at which time decarboxylation began. Flame testing the gas
extinguished a lit splint confirming the presence of CO2. Intermittent heating was continued for approximately two hours at which time two layers had
formed, a vivid burgundy overhead and a thin solid layer on the bottom. The previously milky orange solution was now deep red and completely
transparent. The odor of the solution had changed from a strong floral-grape to a light floral odor with a very distinct amine odor. The solution now
reeked of phenethylamine, although it still had some floral character to it. At this point in time even though the decarboxylation is complete, the
schiffs base complex is still present, as indicated by the vivid red color. Now its time to cleave the schiffs base and collect the goodies! for those
who might not know, water is the enemy of all schiffs bases. Formation of a schiffs base is a hydrolysis reaction, water is split off at the
beginning, and addition of water and or acid to the reaction will drive the reverse reaction back to the starting materials. Here we will take
advantage of this to cleave the complex and get our product. 10 grams DH2O and a small pinch of citric acid were added to the solution and the
solution was once again heated to boiling for 1 hour to break the complex. If one was looking for a hydrochoride salt they would just use concentrated
hydrochloric acid and reflux as normal and after 1 hour they could extract the salt out in the normal fashion. I chose a very small amount of citric
acid so as to avoid hydrochloride formation. Acid is not required but does speed up the process significantly. Just refluxing with DH2O will do the
trick but with my complex (phenethylamine-phenylacetaldehyde) the complex is so strong and stable that the reflux would take 3-4 hours! After the
reflux is complete, there are two layers formed and orangey-yellow upper oily layer and the lower water layer. The upper layer is seperated and dried
over zeolite or magnesium sulfate as you see fit, the oily layer is distilled reclaiming the phenylacetaldehyde and collecting the phenethylamine as
base. The phenethylamine was dried over sodium hydroxide and will be used for a michael reaction with methyl acrylate tonight or tomorrow as soon as I
have the time. A couple of notes: First I couldn't find any spearmint oil around town if you can beleive that, only fake wintergreen which is not the
same thing of course. So I used phenylacetaldehyde because I had it lying around and I know it forms a schiffs base readily. Carvone will work just
fine if you have it. I am currently lining up other experiments using cinnamon oil, vanillin, benzaldehyde, and cyclohexanone. Carvone is an
unsaturated ketone so it will be interesting to see how cyclohexanone performs. Benzaldehyde from almond flavor is very reactive also as well as
vanillin. As soon as I can get them run I will post the info for you. So maybe a day or two. Cinnamon oil contains cinnamaldehyde, an unsaturated
aldehyde, so that should be highly reactive as well.
Now on to the Aza-Michael!!
Best Regards,
SPOOKY
|
|
|
AvBaeyer
National Hazard
   
Posts: 651
Registered: 25-2-2014
Location: CA
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
I find this post lacking in enough detail to make it believable. I believe that it has been fairly well established that aldehydes are poor catalysts
for the decarboxylation of amino acids. Moreover, the reactivity of phenylacetaldehyde should render it one of the poorest aldehydes by a large
margin.
After the hydrolysis of the purported product imine an "oily" layer is formed which supposedly contains phenylacetaldehyde and phenethylamine. The
imine complex is stated to be "so strong and stable." Why wouldn't the products then simply recombine to form the imine? Distillation of the purported
products is claimed but no supporting information is provided for reference (eg., bp).
I think that someone who claims 30 years experience as an organic chemist can do better than what is in this post. I do not believe a word of it.
AvB
|
|
|
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
@AvBaeyer I see what you mean; it seems strange that someone with 30 years experience as an organic chemist couldn't think of a better way to get
benzaldehyde than from almond flavoring. But maybe the work he was doing was so specialized that there's a lot he doesn't know outside of his
specialty? It's a whole different world, working in industry compared to doing this stuff as an amateur.
But if he's still reading this, I'd posit that cyclic enones seem to make far better catalysts than acyclic ones do.
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
Sigmatropic
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 307
Registered: 29-1-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
| Quote: |
The phenethylamine was dried over sodium hydroxide and will be used for a michael reaction with methyl acrylate tonight
|
Hmmmm... where would this be going... not the 4-piperidone derivative I hope.
|
|
|
spookyboo13
Harmless

Posts: 4
Registered: 3-1-2018
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
First and foremost, the object of this work is OTC.. not bought from ebay. Second I have been doing this for quite some time, and have just a little
more experience in the field than the average amateur. The unfortunate thing about leaving the big city is also leaving the big budget companies
behind, and working the hard way, by making almost everything required as opposed to buying it. I could just call alfa for the amine, but as such they
ask a lot of questions i'm not in a position to answer. Anyway benzaldehyde and cinnamaldehyde are an experiment, to further knowledge on the topic,
and both are fairly easy to get. I had a feeling I would take some flack because of my experience but I guess that just goes with the territory.
Whether aldehydes are poor catalysts overall has nothing to do with the fact that phenylacetaldehyde is exceptionally reactive either way and I just
happen to have it lying around, so why not use it. Phenylacetaldehyde forms schiffs bases readily with many nitrogenous compounds, not just
phenylalanine, i' have been working with it for years, even a weak ammonia solution will give a schiffs base with phenylacetaldehyde with just a shake
and no heating required. Lastly, I was in a huge rush to finish the post and get off to work, what reference were you referring to? What other detail
were you looking for anyway, I think enough detail was given for someone who might duplicate the work. This is not the first batch I have run anyway,
more like the sixth, the amine is in hand and ready for the next project, so who cares what you and your duplicate personality think anyway? I have
met a million guys like you over the years, jealous and resentful. Instead of just regurgitating someone else's work try thinking up your own!
SPOOKY
|
|
|
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
Don't take it personally, spooky. We're fairly skeptical of first-time posters here as a rule, especially ones that seem a hair's breadth away from
some sort of illegal drug synthesis. If you want everyone here to take you more seriously, you just have to stick around and post more. If your
posts all look like what we'd expect from a Walter White wannabe, you'll probably get lectured at, ignored, and then banned. If you seem like a
knowledgeable chemist, people will come to trust you more.
If I wanted OTC benzaldehyde, I'd distill this floor leveler/treatment stuff that has a lot of benzyl alcohol in it, then oxidize with potassium
permanganate while stirring vigorously. Then vacuum distill. I was under the impression that the amount in almond flavoring was quite tiny. But
perhaps I'm wrong. In any case, I have half a liter of benzaldehyde somewhere in storage, and probably wouldn't ever need to synthesize it.
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
spookyboo13
Harmless

Posts: 4
Registered: 3-1-2018
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Melgar,
Fair enough, no Walter White wannabee here, after lurking for years, just trying to pass on worthwhile info. If my process was a failure I would post
that as well just so someone knows not to waste their time. Most of my focus is perfumery related.. nothing else.. well nothing else that is organic
chemical anyway.

|
|
|
spookyboo13
Harmless

Posts: 4
Registered: 3-1-2018
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Just for curiousity how do I post a paper, link or otherwise? I have a cool paper on decarboxylation catalyzed by pyridoxal (vitamin b-1) its kind
of expensive but worth investigating. This is where I got the lead for the schiffs base work.
|
|
|
EilOr
Harmless

Posts: 20
Registered: 12-12-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
If smell doesn't bother you - good old genuine terpuntine is OTC a almost perfect solvent for that reaction, giving 90%+ yield of a crude product
after extraction with 5% acetic acid, washing with DCM, freebasing with NaOH, filtration washing with aq. ammonia and later around 60-70% after vacuum
destillation of the tryptamine.
Here some pics of destillation:
http://forum.lambdasyn.org/index.php?topic=1057.0
Tryptamines can be further purified by precpt. as carbamate with CO2 from EtOH or IPA (a household "soda stream" can be used) if necessary
US2943093
|
|
|
LD5050
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 182
Registered: 16-1-2017
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
35.9g of tryptophan was added to a 500ml RBF attached to a reflux condenser. I then added 120ml of turpentine and 31 drops of spearmint oil. Reaction
mixture at this time was milky white heavy with tryptophan precipitate. 5 min into heating the mixture appearance turned slight yellow/cream color. 30
minutes into reflux large "boiling" bubbles erupted and what seemed to be small Co2 bubbles around edges of RBF.
90 minutes in and a lot of small bubbles forming indicating Co2 (I think). 30 minutes later I added 15 more drops of spearmint oil through condenser.
Viscosity of reaction mix seems to have increased. 40 minutes later I added 60ml turpentine + 50 drops of spearmint oil. After addition a lot more
small Co2 bubbles seem to form. 3 hours later I added 20 drops of Spearmint oil. 5 hours later added another 20 drops.
Next morning approx 24 hours into reaction reaction mix is now an orangish color not so much milky/turbid anymore, somewhat transparent possibly
indicating reaction is close to completion? When stirring is stopped small amount of white precipitate collects on bottom of RBF. When stirring is
started back up small bubbles/foam rises almost to top of RBF but then subsides after a few seconds.
25 hours into reflux I stop the heating and let cool to room temp with stirring. I'm now left with a brownish/orange turbid solution at room temp with
small amount of brown oily gunky substance on bottom of flask.
I know need to purify/extract crude tryptamine from reaction mixture but I'm not sure best way to do this. I found a procedure on erowid using vinigar
but I think I would rather vacuum distill if I can but I'm not sure how to go about it. I have a vacuum distillation setup. I'm confused a bit on what
I have in the reaction mixture after decarboxylation of the tryptophan. Do I now have the freebase oil of tryptamine in solution? Would I first
distill off the turpentine then the tryptamine freebase under vacuum then acidity with HCL to form tryptamine HCL? I performed a vacuum distillation a
while back on the tryptamine but I didn't take notes and can't remember what I did but I remember when I was distilling the tryptamine it had
crystallized in the condenser.
So ya I'm a little puzzled on what to do here. I looked around but couldn't find much on distilling the tryptamine from the reaction mix and rather
can only find extraction with vinigar and chloroform. I would rather vacuum distill to get a cleaner product if possible.
|
|
|
Melgar
Anti-Spam Agent
    
Posts: 2004
Registered: 23-2-2010
Location: Connecticut
Member Is Offline
Mood: Estrified
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by spookyboo13  | | Just for curiousity how do I post a paper, link or otherwise? I have a cool paper on decarboxylation catalyzed by pyridoxal (vitamin b-1) its kind
of expensive but worth investigating. This is where I got the lead for the schiffs base work. |
If you're doing the "quick reply" at the bottom of the page, click "preview post", and it'll take you to the full editor. There, you'll see an
attachment box that you can use to attach pictures or documents, or whatever you want.
The first step in the process of learning something is admitting that you don't know it already.
I'm givin' the spam shields max power at full warp, but they just dinna have the power! We're gonna have to evacuate to new forum software!
|
|
|
Chemi Pharma
Hazard to Others
  
Posts: 350
Registered: 5-5-2016
Location: Latin America
Member Is Offline
Mood: Quarantined
|
|
Hi everyone,
I was avoiding enter in this discussion board cause, really, until a few days ago, I think I didn't have too much knowledge to discuss the topic.
However I was forced to study the theory of decarboxylation of aminoacids cause a project I have that uses pyrrolidine and I conclude the better way
to sinthesize it is decarboxylating L-Proline.
Then, I search at Google and here at the forum and found very interesting materials about aminoacids decarboxylation I want to share with you guys.
At first, I looked at an old thread that had begun by Scr0t in 2015, where he teached how to decarboxylate L-Proline with even 85% yield, using
acetophenone as a ketone, no solvent at all, just adding L-Proline and reflux the mix at 150ºC. He told, thereafter, about the easy workup either.
He covered the use of spearmint oil and turpentine as a solvent too, as a carvone catalysed decarboxylation, mentioning the eventual use of DMSO to
help solvating the mix.
I quoted what he'd wrote below to be more clear:
Quote: Originally posted by Scr0t  | Several different methods of decarboxylation were applied to the amino-acid l-proline in attempts to obtain the cyclic secondary amine pyrrolidine.
Pyrrolidine can substitute piperidine in many applications.
Copper catalysed decarboxylation
50.0g l-proline mixed with 5.0g basic copper carbonate Cu2(OH)2CO3 [1] and heated directly over an
electric hotplate (~1.5kW).
When plate temperature was ~320°C a small amount of product came across (going by smell but had obvious water contamination) but was very slow. It
was not until plate temperature was ~420°C when collection rate picked-up (~1 drop every 1-2s), the collected product was a pale yellow colour and
smelled 'charred', collection was continued at 420-450°C for about 3hrs when it slowed considerably yet the contents in the distilling flask was
still significant [2].
The collected material was dried over a few grams of solid NaOH and then distilled, the material collected between 85-89°C weighed 3.1g Yield
of pyrrolidine 10%.
A clear higher boiling point residue was left behind (bp >90°C, ~15ml) in the distilling and was not examined further.
Overall the reaction was very low yielding, required a higher temperature and was sluggish compared to the decarboxylation of niacin to pyridine with
the same catalyst loading.
Copper carbonate is not an effective catalyst for decarboxylation of this substrate and the results are probably no better than
simply heating the proline on its own.
[1] If the mixture is allowed to stand at room temperature for ~24hrs it darkens to a deep blue colour.
[2] Proline reportedly decomposes at its melting point ~200°C, decarboxylation is evidently only a minor component of this.
----------------------------------
Acetophenone catalysed decarboxylation
20.00g l-proline in 80ml acetophenone was set for reflux and heated in an oil bath to 150°C
At ~130°C evolution of CO2 commenced, generation of some water and a mild smell of pyrrolidine from the top of the condenser was noticed.
Over the course of the reaction the solids dissolved and the reaction progressed to a deep orange colour, CO2 evolution rapidly abated at
around 40mins and at 50mins it was removed from the heat.
30ml 36% HCl made up to 100ml was added to the cooled mixture and stirred for 30mins (white mist formed on addition due to the presence of freebase
vapour), the lower aqueous phase was separated and the acetophenone layer washed with 50ml H2O containing a few grams of NaCl to aid with
phase separation, the combined aqueous portions were washed with 2x20ml DCM.
The aqueous phase was cautiously treated with 20g NaOH in 30ml H2O whereupon a separate upper phase formed however this was not
primarily pyrrolidine.
The mixture was distilled with stirring to collect the product and some water (<=92°C), the upper phase that formed earlier remained in the
distillation flask as a few millilitres of a brown viscous oil/goo when cool.
The distillate was treated with a couple of grams of solid NaOH and the upper phase separated and distilled (bp 87°C) to yield 10.85g
pyrrolidine (85%).
----------------------------------
Carvone catalysed decarboxylation
Into a 1L RBF 50.0g l-proline, 500ml turpentine and 2.0g spearmint oil was added and with stirring it was refluxed in an oil bath (~180°C). The
mixture was heated to a rapid reflux (145-160°C).
At 20hrs there was still a few small lumps of what appeared to be unreacted proline in suspension [1] but the reaction was removed
from the heat and allowed to cool. The mixture was treated with 60ml 36% HCl made up to 200ml with H2O and stirred for ~15min.
The mixture was separated (small amount of brown gummy material at the interface), washed with DCM, treated with 40g NaOH in 100ml H2O and
then the whole distilled to collect the product and water. The distillate was treated with a few grams of solid NaOH [2], separated
and distilled to yield 25.2g (82%) pyrrolidine.
The spearmint oil used was the same as that used for successful decarboxylation of tryptophan, the slow reaction is possibly due to a low solubility
of proline in this solvent. Inclusion of some DMSO may improve reaction time.
[1] These lumps turned out to be quite gooey, possibly some proline surrounded by a side-product precipitate.
[2] The two-phase mixture of aqueous NaOH and distillate turned to a pink colour on standing in air.
|
Further, I found a paper that elucidates the mechanism of the Schift bases formation between the aminoacids and ketones and the hydrolises to amino
hidrochloride salts, with a nice experimental section, that's attached below.
Attachment: Decarboxylation by heat of a-Amino-acids in the Presence of Ketones.PDF (642kB)
This file has been downloaded 1324 times
And searching a little more I found another paper that covers the decarboxylation of aminoacids at room temperature by N-bromosuccinimide followed by
reduction of the nitrile formed with nickel chloride and sodium borohydride (Nickel Boride, my favorite reducting agent ). Attached below either. ). Attached below either.
Attachment: aminoacids decarboxylation to nitriles and further reduction to amines with n-bromosuccnimide and nickel boride.PDF (66kB)
This file has been downloaded 620 times
I hope had brought something interesting to this discussion board guys
|
|
|
Chemical1mbalance
Harmless

Posts: 1
Registered: 22-1-2019
Member Is Offline
|
|
100g Xylitol placed in reaction vessel and heated to 130C. It seems to reach an easily workable viscosity at this temperature.
Added 2mL Spearmint oil
Added 5g Tryptophan in small increments, it seemed to form a layer on top and not want to mix in when added all at once.
Contents appear cream colored much like the PG mixture, now the heat is turned up. Right around 160C the mixture turns completely transparent with a
orangish color to it. No bubbling was ever really noticed, but a really strong smell of tryptamine was noted. Continued heating thinking maybe at
some point bubbling would commence, but it never did all the way up to 200C. Let mixture cool down and it turned into a clear amber colored jelly
that smelled of tryptamine. When mixed with hot water the jelly dissolved and a whitish colored precipitation was forming and falling to the bottom.
Never got a chance to test it, but I suspect it could have been tryptamine based on solubility.
Perhaps someone else with a little more knowledge may want to test this out as Xylitol is cheap, easy to work with, and pretty inert as far as sugar
alcohols go. Also isn't supposed to have any carmelization reactions.
What I don't know is if at 160C a decarboxylation is taking place or if it is suddenly becoming soluble into the Xylitol...
[Edited on 23-1-2019 by Chemical1mbalance]
|
|
|
oblivionbubble
Harmless

Posts: 21
Registered: 30-8-2019
Member Is Offline
|
|
I have studied the decarboxylation of tryptophan to tryptamine for quite some time now.
I read everything on Rhodium Archive, several threads here and other forums, and quite a few papers.
There seems to be a handful of contradictory information in the mentioned resources i studied. So now I am left confused and do not know how to
proceed.
Can someone help me out with recommendation on the best setup to use, given availability of chemicals.
Acetophenone was recommended, but looking the several synthesis I currently dont have the means to produce it.
| Quote: |
Ketone-catalyzed decarboxylation, as described by Drone #342:
Decarboxylation is accomplished by mixing about 80 g tryptophan in 250 mL of high-boiling solvent (xylene, DMSO, cyclohexanol, etc.), adding a
dash of a ketone (I like 5 g of cyclohexanone, but a couple grams of MEK works reasonably well), heat it to around 150 deg, and when evolution of CO2
ceases/solution is clear, the reaction is complete. This takes anywhere from 1.5 to 4 hours. After this is over, the solvent is boiled off (or at
least greatly reduced in volume), and the residue is dissolved in DCM. This is washed with a 5% NaHCO3 solution, then a distilled water solution, then
the DCM layer is separated off, dried with MgSO4, and the DCM is boiled off. You now have reasonably pure tryptamine. |
I used DMSO and cyclohexanone... I took almost 3 days for the bromine (amber) colored solution to become translucent. Ihad no idea how to reduce the
DMSO amount significantly?
First run was a trainwreck, as i missed the no oxygen line. Ended up with weird mud.
2nd attempt was better, with a reflux condenser attached, however i had no way of verifying if the product indeed is tryptamine. Any tips on that?
Colorimetric reagents are useless, TLC ? I can submit it for laboratory analysis. I measured the gas evolution using a condom zip tied to the side
neck. I guess a balloon would be a bit more stylish.
Solvents available:
Turpentine, DMF, Tetrahydronaphtalene, Acetonitrile, White Spirit, Mineral Oil, Isopropyl ether
Catalysts: acetone, cyclohexanone, Methyl-Iso-hutyl ketone
Also> Could I use the same procedure for melatonine and 5-HTP?
Thank you
|
|
|
oblivionbubble
Harmless

Posts: 21
Registered: 30-8-2019
Member Is Offline
|
|
Just a quick follow up. I decided to do the following:
In a 2L FBF (flat bottom flask?), placed on a magnetic hotplate, there was added 500 ml tetrahydronaphtalene, 160 g of tryptophan and a stir bar of
suitable size.
Set the temp to 300 C and decent stirring.
For covering the top, i managed to find some sort of a gas preparation adapter which neatly closed the flask, yet allowed gas discharge through
miniature opening.
I used Methyl-Iso-Butyl-Ketone, around 10 ml in the beggining and then several additions of couple mls as the end of the reaction was noowhere to be
seen.
Now it seems like we are coming to the end, after around 24 hours at 150 / 300 degrees C.
Will provide the workup and yield.
P.S.
Ran a smaller scale decarboxylation with technical grade "white spirit" and cyclohexanone, which was complete after several h and provided
satisfactory results.
|
|
|
Pumukli
National Hazard
   
Posts: 708
Registered: 2-3-2014
Location: EU
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
There should be a TLC method for identification. p-dimethylamino-benzaldehyde -as I remember- can be used for indoles.
What is 150/300 degrees C? Hotplate was set to 300C but the mixture was refluxing at 150C or what?
|
|
|
| Pages:
1
2
3 |