Originally posted by Lego
Molecular interaction of serotonin 5 HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with super-potent N-benzyl phenethylamine
agonists
Braden MR, Parrish JC, Naylor JC, Nichols DE
Mol. Pharmacol., 2006 http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/mol.106.028720
Abstract: Experiments were conducted to examine the molecular basis for the high affinity and potency of a new class of 5 HT2A
receptor agonists, N-benzyl phenethylamines. Competition binding assays at several serotonin receptors confirmed that an N-arylmethyl substitution was
necessary for affinity increases up to 300-fold over simple N-alkyl homologues, as well as enhanced selectivity for 5 HT2A vs. 5-HT2C and 5-HT1A
receptors. PI hydrolysis functional assays confirmed that these N-benzyl phenethylamines are potent and highly efficacious agonists at the rat 5 HT2A
receptor. Virtual docking of these compounds into a human 5 HT2A receptor homology model indicated that the N-benzyl moiety might be interacting with
F339((6.51)), whereas the phenethylamine portion was likely interacting with F340((6.52)). Experiments in h5 HT2A receptors with F339((6.51))L and
F340((6.52))L mutations appear to support this hypothesis. Dramatic detrimental effects on affinity, potency, and intrinsic activity were observed
with the F339((6.51))L mutation for all N-benzyl analogues, whereas most N-unsubstituted phenethylamines and traditional agonists were only weakly
affected, if at all. Consistent with other published studies, the F340((6.52))L mutation detrimentally affected affinity, potency, and intrinsic
activity of nearly all compounds tested, although a strong change in intrinsic activity was not seen with most N-aryl analogues. These data further
validate the topology of our h5 HT2A receptor homology model. Importantly, this study is the first to identify a hitherto unrecognized role for
residue 6.51 in agonist activation of a serotonin GPCR, whereas most previous reports have suggested a varied and sometimes contradictory role in
homologous GPCRs.
* Full details of chemical syntheses of all novel compounds and characterization of additional analogues will be described elsewhere
* By contrast, the N-benzyl group produced a profound increase in affinity (ca. 7- to 300-fold) and potency (ca. 100- to 200-fold) at the r5-HT2A
receptor. Addition of a polar methoxy or hydroxy group at the 2-position of the benzyl group further increased affinities |



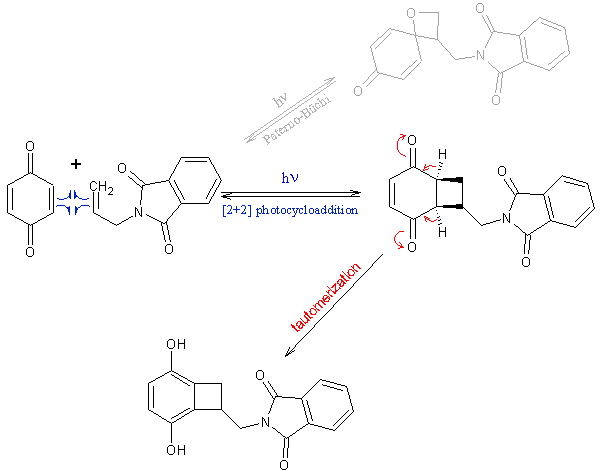
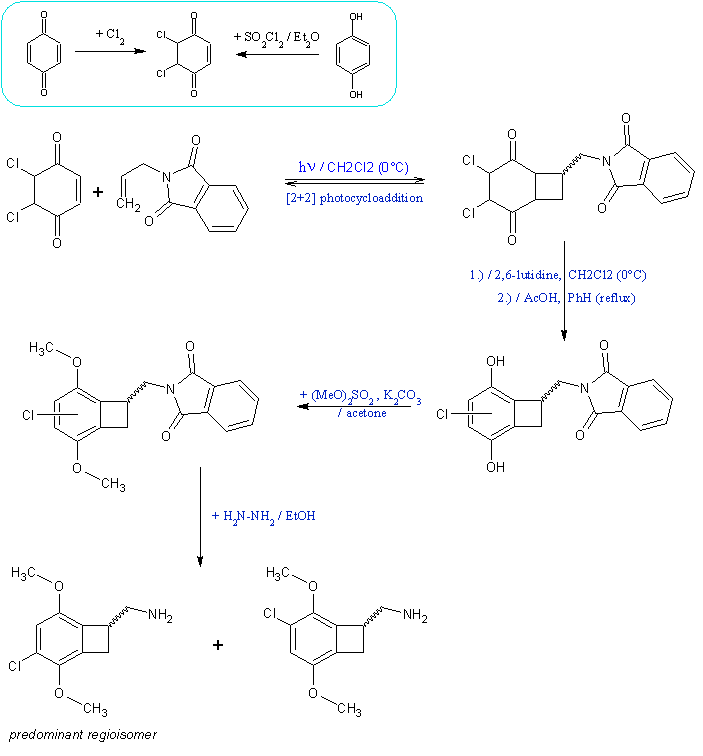
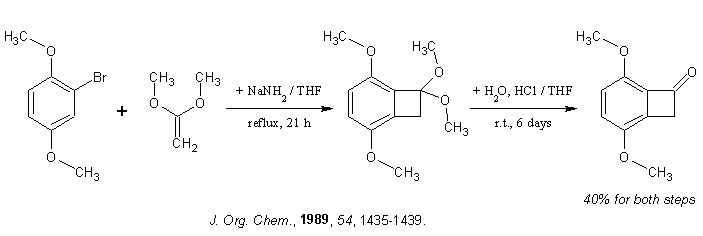
 . However, 3-methyl-2-cyclohexenone reacts smoothly with
ethylene[1] as does plain cyclohexenone (90% yield), undesired Paterno-Büchi heterocycle is formed only in 3%
yield[2]. Another procedure[3] uses electron-rich olefin (note also interesting fragmentation). I did consider
acroylnitrile, but wouldn't the use of isolated alkene minimize side-reactions (dimerizations), since in that case only enone can be light-excited? I
see no frontier orbital obstacle to have isolated olefin as one of the components.
. However, 3-methyl-2-cyclohexenone reacts smoothly with
ethylene[1] as does plain cyclohexenone (90% yield), undesired Paterno-Büchi heterocycle is formed only in 3%
yield[2]. Another procedure[3] uses electron-rich olefin (note also interesting fragmentation). I did consider
acroylnitrile, but wouldn't the use of isolated alkene minimize side-reactions (dimerizations), since in that case only enone can be light-excited? I
see no frontier orbital obstacle to have isolated olefin as one of the components.