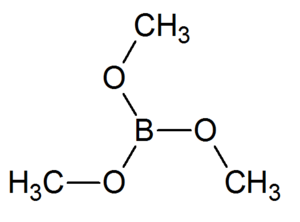
Trimethyl borate
Trimethyl borate is a boron triester consisting of a single boron atom bound to three methoxide groups. It is a volatile liquid that ignites easily to give a brilliant green flame, purer than one of barium or copper. It may be produced readily in large quantities.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Trimethyl borate, being produced by dehydration, decomposes into methanol and boric acid on exposure to water. It is a reducing agent and burns in the presence of oxygen to form boron trioxide. In flames, it emits a brilliant green color that overpowers many other flame colors, as evidenced here.
Physical
Trimethyl borate is a colorless liquid at room temperature, that evaporates easily. It has a melting point of −34 °C and boils at 68 °C. It will decompose in water.
Availability
Relatively pure trimethyl borate can be bought from only a few chemical suppliers as it has few commercial applications. It is by far cheaper and more practical to produce it.
Preparation
Trimethyl borate can be produced by adding an excess of dry methanol to boric acid or, preferably, boric oxide, with a small amount of sulfuric acid and/or some heating to dehydrate the mixture if needed.
Projects
- Green flames
- Making sodium borohydride
Handling
Safety
There is little data on the toxicity of trimethyl borate. Nevertheless, it is a good idea not to consume or inhale it. Keep away from open flame. Water may be used to put out trimethyl borate flames. When igniting trimethyl borate, goggles should be worn to prevent boric oxide dust from irritating the eyes.
Storage
Trimethyl borate should only be stored in closed bottles, away from light or any heat source.
Disposal
Trimethyl borate can be safely burned. It will hydrolyze in water to yield methanol and boric acid, which can be safely disposed of.