Ethyl formate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl formate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethyl methanoate | |
| Other names
Areginal
Ethyl formiate Formic acid ethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 74.08 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fruity, rum or raspberry-like |
| Density | 0.917 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −80 °C (−112 °F; 193 K) |
| Boiling point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| 10.5 g/100 ml (at 20°C)[1] | |
| Solubility | Miscible with acetone, benzene, diethyl ether, ethanol, THF |
| Vapor pressure | 200 mmHg (20°C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Mathesongas |
| Flash point | -20 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
1850 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1110 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 2075 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) |
| LC50 (Median concentration)
|
10,000 ppm (cat, 1.5 hr) 8000 ppm (rat, 4 hr) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Methyl formate Methyl acetate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
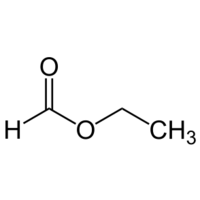
Ethyl formate or ethyl methanoate is a volatile ester obtained from ethanol and formic acid, with a pleasant fruity smell, reminiscent of rum or raspberry. It has the formula HCOOCH2CH3 or C3H6O2.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Ammonia reacts with ethyl formate to give formamide:
- HCOOCH2CH3 + NH3 → HCONH2 + CH3CH2OH
Physical
Ethyl formate is a colorless volatile liquid, with a fruity rum-like odor, poorly soluble in water but miscible with many organic solvents.
Availability
Ethyl formate can be purchased from chemical suppliers and online.
Preparation
Ethyl formate is best synthesized by the Fischer esterification between conc. formic acid and anh. ethanol, in the presence of a desiccant, such as anhydrous calcium chloride, under reflux. The resulting impure ethyl formate can be purified by adding it in cold water and then extracted using a separatory funnel and dried with anhydrous calcium chloride or sodium sulfate.
Another route involves treating sodium formate (which can be obtained from the haloform reaction of ethanol or isopropanol) with anhydrous ethanol and concentrated sulfuric acid.[3]
The industrial route involves the reaction of ethanol with carbon dioxide in an autoclave at 100-125 °C and 200 for 10-20 hours, in inert conditions, in the presence of gold supported on titanium dioxide catalyst.[4] However this route is not feasible for the amateur chemist.
Projects
- Organic extractions
- Make formamide
Handling
Safety
Ethyl formate is irritant if inhaled. It is also very flammable.
Storage
In closed bottles, away from ignition sources
Disposal
Ethyl formate can be safely disposed of by burning it outside or in an incinerator.
References
- ↑ http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_card_id=0623
- ↑ Tabuchi; Journal of Chemical Physics; vol. 28; (1958); p. 1014,1018
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/file.PostFileLoader.html?id=56e532e0dc332d21e773a9ca&assetKey=AS%3A339109211066368%401457861344459.
- ↑ http://www.google.com/patents/US20130102807
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
- Chemical pages without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Organic compounds
- Formates
- Esters
- Solvents
- Polar solvents
- Aprotic solvents
- Fragrant compounds
- Volatile chemicals
- Materials unstable in basic solution
- Liquids