Xylene
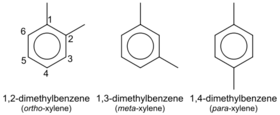 The three xylene isomers.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dimethylbenzene
| |
| Other names
Methyltoluene
Xylol | |
| Properties | |
| C8H10 C6H4(CH3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 318.504 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Aromatic, paint thinner-like |
| Density | 0.864 g/mL |
| Melting point | −47.4 °C (−53.3 °F; 225.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 138.5 °C (281.3 °F; 411.6 K) |
| 0.0106 g/100 ml (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Miscible with acetone, benzene, diethyl ether, esters, ethanol, toluene |
| Vapor pressure | 6.65-8.80 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich (mixture) Sigma-Aldrich (ortho) Sigma-Aldrich (meta) Sigma-Aldrich (para) |
| Flash point | 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Benzene Toluene |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of a benzene ring with two methyl substituents. Xylene consists of three isomers: ortho-xylene, meta-xylene and para-xylene, each having a molecular formula C8H10 or, since it's an aromatic compound, C6H4(CH3)2, in order to highlight the aromatic ring.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Xylene can be nitrated to give mono-, di-, trinitroxylene (TNX), using a mixture of sulfuric and nitric acid.
Physical
All three isomers of xylene are colorless liquids at room temperature and have a characteristic paint thinner smell. The melting point of the three isomers ranges is −25 °C for o-xylene, −47.87 °C for m-xylene and 13.26 °C for p-xylene. The boiling point for each isomer is 144 °C for o-xylene, 139 °C for m-xylene and 138 °C for p-xylene. The density of each is around 0.88 g/mL for o-xylene and 0.86 g/ml for meta and p-xylene.
Availability
Xylene is available as a paint thinner, either pure or mixed with other low chain hydrocarbons, as well as traces of butanol or butyl acetate and it's always a mixture of the three isomers. It can also be carefully removed from mixed solvents commonly found in hardware stores by fractional distillation.
Individual isomers can be purchased from chemical suppliers, though they aren't cheap. Because the boiling point of the three isomers is very close, it's extremely difficult to separate the three isomers via fractional distillation.
Technical grade mixed xylenes often contains 6-20% ethyl benzene as an impurity. This usually isn't a problem unless xylene is used for purification or sensitive reactions. Dimethylthiophenes are another common type of impurity, which can be removed by shaking repeatedly with small portions of concentrated sulfuric acid until the acid layer remains clear.
Preparation
Xylene can be prepared by methylating toluene, a process that yields all the three isomers.
Projects
- Organic extraction
- Sulfur extraction
- Tetranitroxylene synthesis
- Phthalic anhydride or phthalic acid from ortho-xylene
- Separation of xylene isomers
Handling
Safety
Xylene is an irritant to eyes, nose and lungs. It has low toxicity and low carcinogenic potential. Xylene is flammable and should be handled with care.
Storage
Xylene should be stored in closed bottles, away from any source of heat and light.
Disposal
Xylene can be burned, though this will generate lots of carbon monoxide, soot, VOCs, PAHs, as well as unburnt xylene. If you really want to do burn it, do it outside, away from people. Try not to burn too much xylene at once, and instead burn it in small amounts over a longer period of time, preferably diluted with a more "clean" burning solvent, like (denaturated) alcohol.
As it is an aromatic compound, Fenton's reagent can also be used. While the oxidation doesn't produce harmful products, the process produces lots of gasses which will aerosolize some of the unoxidized xylene, as well as other intermediate products into the air. This is dangerous in an enclosed area, carrying both a fire/explosion hazard as well as inhaling irritant xylene vapors. To reduce this unpleasant effect, xylene should be added dropwise or bubbled through a gas diffusing stone in the Fenton solution to limit vapor escape. The neutralization should be performed in a fumehood, well ventilated area or outside. Using a UV lamp will improve the speed of decomposition.[1]