Borax
From Sciencemadness Wiki

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Sodium borate | |
| Other names
Disodium tetraborate
Sodium tetraborate | |
| Properties | |
| Na2B4O7 (anhydrous) Na2B4O7·10H2O (decahydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 381.38 g/mol (decahydrate) 201.22 g/mol (anhydrate) |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.73 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 743 °C (1,369 °F; 1,016 K) (anhydrous) |
| Boiling point | 1,575 °C (2,867 °F; 1,848 K) |
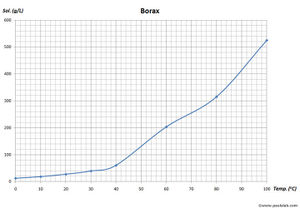
| 2.7 g/100 ml (20 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethylene glycol, glycerol Moderate soluble in diethylene glycol, methanol Slightly soluble in acetone, ethanol, ethyl acetate |
| Vapor pressure | ~0 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Boric acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Borax or sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, is an important boron compound. It has the chemical formula Na2B4O7.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Sodium borate will react with a strong acid to release boric acid.
Physical
Borax is a white crystalline solid. It melts at 743 °C and boils at 1,575 °C. It has a density of 1.73 g/cm3.
Availability
Borax is sold by various chemical suppliers.
It is also sold in various pharmacies and iron forgeries.
Preparation
Sodium borate can be made by reacting boric acid with a sodium compound.
Projects
- Make boric acid
- Grow borax crystals,borax snowflakes
Handling
Safety
Borax has low toxicity.
Borax was added to the Substance of Very High Concern (SVHC) candidate list on 16 December 2010 in the EU.
Storage
Borax should be stored in closed bottles
Disposal
Sodium tetraborate can be dumped in trash.