Chloroacetamide
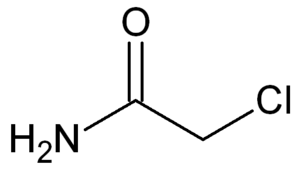 Structure of chloroacetamide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Chloroacetamide
| |
| Other names
Chloracetamide
Chlorocetamide | |
| Properties | |
| C2H4ClNO | |
| Molar mass | 93.51 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless or pale yellow solid |
| Melting point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| Boiling point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) (decomposition)[1] |
| 9.8 g/100 ml (20 °C) 9.0 g/100 ml (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol Insoluble in diethyl ether |
| Vapor pressure | 0.05 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 170 °C (338 °F; 443 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
138 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Acetamide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chloroacetamide or 2-chloroacetamide is a chlorinated organic compound with the molecular formula C2H4ClNO or ClCH2CONH2. It is used in the manufacturing of herbicides.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Chloroacetamide is used to add an acetamide functional group to organic compounds.
Phosphorus pentoxide will dehydrate chloroacetamide to chloroacetonitrile.[2]
Addition of a strong base, like NaOH, will produce glycolic acid derivates.
Physical
Chloroacetamide is a colorless solid although older samples appear yellow. It has a characteristic odor and is readily soluble in water and in some organic solvents.
Availability
Chloroacetamide is sold by chemical suppliers.
Some herbicides contain chloroacetamide.
Preparation
Chloroacetamide is produced by ammonolysis of esters of chloroacetic acid. For example, by stirring ethyl chloroacetate with aq. ammonia at low temperatures (0–5°), as higher temperatures favor the replacement of the chlorine, forming glycine and its esters, which lowers the yield.[3]
- ClCH2CO2CH2CH3 + NH3 → ClCH2C(O)NH2 + CH3CH2OH
- ClCH2CO2CH2CH3 + 2 NH3 → H2NCH2COOH + NH4Cl + CH3CH2OH
A less known route involves the reaction of ethenone with nitrogen trichloride at -60 °C, in anhydrous conditions.[4]
Projects
- Preparation of chloroacetonitrile
- Synthesis of Modafinil
- Make herbicides
Handling
Safety
Chloroacetamide is toxic, irritates eyes and skin, and may cause an allergic reaction. It is suspected of reproductive toxicity and teratogenicity.
Storage
Should be kept in airtight glass of plastic bottles, away from light, moisture or air.
Disposal
Can be neutralized with a solution of NaOH or KOH to less harmful products, diluted and poured down the drain.
References
- ↑ Bisschopinck; Chemische Berichte; vol. 6; (1873); p. 734
- ↑ http://orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=CV4P0144
- ↑ http://orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv1p0153
- ↑ Coleman; Peterson; Goheen; Journal of the American Chemical Society; vol. 58; (1936); p. 1876