Difference between revisions of "Ascorbic acid"
(→Availability) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
| − | + | {{Chembox | |
| + | | Name = Ascorbic acid | ||
| + | | Reference = | ||
| + | | IUPACName = | ||
| + | | PIN = | ||
| + | | SystematicName = | ||
| + | | OtherNames = | ||
| + | <!-- Images --> | ||
| + | | ImageFile = L-Ascorbic acid structure.png | ||
| + | | ImageSize = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt = | ||
| + | | ImageName = | ||
| + | | ImageCaption = The structure of ascorbic acid. | ||
| + | | ImageFile1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt1 = | ||
| + | | ImageName1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFile2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt2 = | ||
| + | | ImageName2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFile3 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize3 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt3 = | ||
| + | | ImageName3 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR2 = | ||
| + | <!-- Sections --> | ||
| + | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | 3DMet = | ||
| + | | Abbreviations = | ||
| + | | SMILES = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| + | | AtmosphericOHRateConstant = | ||
| + | | Appearance = White solid | ||
| + | | BoilingPt = | ||
| + | | BoilingPtC = | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | Density = | ||
| + | | Formula = | ||
| + | | HenryConstant = | ||
| + | | LogP = | ||
| + | | MolarMass = | ||
| + | | MeltingPt = | ||
| + | | MeltingPtC = | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | pKa = | ||
| + | | pKb = | ||
| + | | Solubility = | ||
| + | | SolubleOther = | ||
| + | | Solvent = | ||
| + | | VaporPressure = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | ||
| + | | Coordination = | ||
| + | | CrystalStruct = | ||
| + | | MolShape = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section4 = {{Chembox Thermochemistry | ||
| + | | DeltaGf = | ||
| + | | DeltaHc = | ||
| + | | DeltaHf = | ||
| + | | Entropy = | ||
| + | | HeatCapacity = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section5 = {{Chembox Explosive | ||
| + | | ShockSens = | ||
| + | | FrictionSens = | ||
| + | | DetonationV = | ||
| + | | REFactor = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section6 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| + | | AutoignitionPt = | ||
| + | | ExploLimits = | ||
| + | | ExternalMSDS = | ||
| + | | FlashPt = | ||
| + | | LD50 = | ||
| + | | LC50 = | ||
| + | | MainHazards = | ||
| + | | NFPA-F = | ||
| + | | NFPA-H = | ||
| + | | NFPA-R = | ||
| + | | NFPA-S = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section7 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| + | | OtherAnions = | ||
| + | | OtherCations = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction_label = | ||
| + | | OtherCompounds = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
'''Ascorbic acid '''is a naturally-occurring organic compound more routinely known as vitamin C. It is found naturally in many fruits and is a well-known antioxidant. It can be easily purchased in tablet or powder form in groceries or pharmacies. In the field of chemistry, it is used as a [[reducing agent]], such as in the precipitation of elemental [[copper]] from a solution of copper(II) ions, as well as a means of introducing the [[ascorbate|ascorbate ion]]. | '''Ascorbic acid '''is a naturally-occurring organic compound more routinely known as vitamin C. It is found naturally in many fruits and is a well-known antioxidant. It can be easily purchased in tablet or powder form in groceries or pharmacies. In the field of chemistry, it is used as a [[reducing agent]], such as in the precipitation of elemental [[copper]] from a solution of copper(II) ions, as well as a means of introducing the [[ascorbate|ascorbate ion]]. | ||
Revision as of 17:48, 14 April 2017
 |
This article is a stub. Please help Sciencemadness Wiki by expanding it, adding pictures, and improving existing text.
|
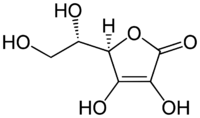 The structure of ascorbic acid.
| |
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White solid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ascorbic acid is a naturally-occurring organic compound more routinely known as vitamin C. It is found naturally in many fruits and is a well-known antioxidant. It can be easily purchased in tablet or powder form in groceries or pharmacies. In the field of chemistry, it is used as a reducing agent, such as in the precipitation of elemental copper from a solution of copper(II) ions, as well as a means of introducing the ascorbate ion.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Ascorbic acid can be used to reduce silver nitrate to metallic silver.
Physical
Ascorbic acid is a white to light yellow solid, soluble in water, with a sour taste. It is soluble in water, less so in alcohols, glycerol, propylene glycol, and insoluble in benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether, petroleum ether, as well as fats and oils.
Availability
Ascorbic acid is sold in pharmacies an most food stores.
Preparation
Ascorbic acid can be extracted from fruits.
Projects
- Reduce various metals compounds to their respective metals
Handling
Safety
Ascorbic acid is vital to the organism. Lack of ascorbic acid leads to scurvy.
Storage
In closed bottles.
Disposal
Ascorbic acid can be safely poured down the drain, dumped in soil or burned.