Difference between revisions of "Borax"
| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| − | Sodium borate can be made by reacting boric acid with sodium hydroxide, under continuous stirring. | + | Sodium borate can be made by reacting boric acid with [[sodium hydroxide]], under continuous stirring. |
:4 H<sub>3</sub>BO<sub>3</sub> + 2 NaOH → Na<sub>2</sub>B<sub>4</sub>O<sub>7</sub> + 7 H<sub>2</sub>O | :4 H<sub>3</sub>BO<sub>3</sub> + 2 NaOH → Na<sub>2</sub>B<sub>4</sub>O<sub>7</sub> + 7 H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
Latest revision as of 15:32, 9 May 2022

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Sodium borate | |
| Other names
Disodium tetraborate
Sodium tetraborate | |
| Properties | |
| Na2B4O7 (anhydrous) Na2B4O7·10H2O (decahydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 381.38 g/mol (decahydrate) 201.22 g/mol (anhydrate) |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.73 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 743 °C (1,369 °F; 1,016 K) (anhydrous) |
| Boiling point | 1,575 °C (2,867 °F; 1,848 K) |
| 2.7 g/100 ml (20 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethylene glycol, glycerol Moderate soluble in diethylene glycol, methanol Slightly soluble in acetone, ethanol, ethyl acetate |
| Vapor pressure | ~0 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Boric acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Borax or sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, is an important boron compound. It has the chemical formula Na2B4O7.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Sodium borate will react with a strong acid to release boric acid.
- Na2B4O7·10H2O + 2 HCl → 4 H3BO3 + 2 NaCl + 5 H2O
Addition of hydrogen peroxide, sodium hydroxide to sodium borate pentahydrate will give sodium perborate.
- Na2B4O7·5 H2O + NaOH + 2 H2O2 → Na2B2O4(OH)4 + NaOH + 5 H2O + 3/2 O2
When borax is added to a flame, it gives a yellow-green color. Since the yellow flame of sodium is undesired, boric acid is used in fireworks instead of borax for green flame and as solution in methanol for pure green flames.
Borax is a prime material in the manufacturing of borosilicate glass. Unlike boric acid, it is not volatile and can be used in high temperature chemical reactions as a source of boron.
Physical
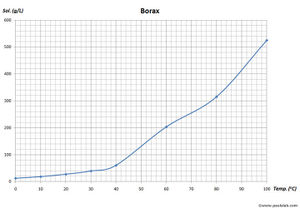
Borax is a white crystalline solid. It is odorless, and has an unpleasant taste. Borax melts at 743 °C and boils at 1,575 °C. It has a density of 1.73 g/cm3. Borax is poorly soluble in cold water, but it's solubility increases with temperature. It is soluble in some organic solvents, like ethylene glycol, glycerol, while moderate soluble in diethylene glycol, methanol. Borax is only slightly soluble in more common solvents like acetone, ethanol, ethyl acetate.
Availability
Borax is sold by various chemical suppliers. Can also be acquired online.
It is also sold in various pharmacies and iron forgeries.
Preparation
Sodium borate can be made by reacting boric acid with sodium hydroxide, under continuous stirring.
- 4 H3BO3 + 2 NaOH → Na2B4O7 + 7 H2O
Projects
- Make boric acid
- Grow borax crystals, borax snowflakes
- pH buffer
- Water-softening agent
- Flux for melting metals
- Borax method (gold extraction)
- Fire retardant
- Make sodium perborate
- Curing agent (leather)
Handling
Safety
Borax has low toxicity. It is only mildly irritant to skin.
Borax was added to the Substance of Very High Concern (SVHC) candidate list on 16 December 2010 in the EU.
Storage
Borax should be stored in closed bottles
Disposal
Sodium tetraborate can be dumped in trash.