Difference between revisions of "Sulfanilic acid"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| ImageAlt = | | ImageAlt = | ||
| ImageName = | | ImageName = | ||
| − | | ImageFile1 = | + | | ImageCaption = |
| − | | ImageSize1 = | + | | ImageFile1 = Sulfanilic acid skeletal structure.png |
| + | | ImageSize1 = 250 | ||
| ImageAlt1 = | | ImageAlt1 = | ||
| ImageName1 = | | ImageName1 = | ||
| Line 92: | Line 93: | ||
| ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/mEjMFW8/sulfanilic-acid-sa.pdf Sigma-Aldrich] | | ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/mEjMFW8/sulfanilic-acid-sa.pdf Sigma-Aldrich] | ||
| FlashPt = | | FlashPt = | ||
| − | | LD50 = 12 | + | | LD50 = 12,300 mg/kg (rat, oral)<br>6.000 mg/kg (rat, IV) |
| LC50 = | | LC50 = | ||
| MainHazards = Irritant | | MainHazards = Irritant | ||
| Line 108: | Line 109: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
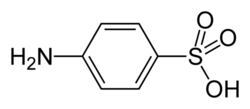
| − | '''Sulfanilic acid''' is an arylsulfonic acid that is mainly used as a precursor for making azo | + | '''Sulfanilic acid''' is an arylsulfonic acid that is mainly used as a precursor for making [[azo dye]]s, such as [[methyl orange]], and sulfa drugs, such as [[sulfanilamide]]. It is also used in the quantitative analysis of [[nitrate]] and [[nitrite]] ions. It can be synthesized easily by sulfonation of [[aniline]] with concentrated [[sulfuric acid]]. |
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
| Line 124: | Line 125: | ||
==Projects== | ==Projects== | ||
| − | Synthesis of [[azo | + | *Synthesis of [[azo dye]]s: |
| − | + | **[[Methyl orange]] | |
| − | + | **[[Acid orange 7]] | |
| − | Synthesis of [[sulfanilamide]] | + | **[[Chrysoine resorcinol]] |
| + | **[[Tartrazine]] | ||
| + | *Synthesis of [[sulfanilamide]] | ||
==Handling== | ==Handling== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:33, 30 November 2022

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Properties | |
| C6H7NO3S C6H4(NH2)(SO3H) | |
| Molar mass | 173.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | Off white or purple crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.485 g/cm3 (25 °C) |
| Melting point | 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K) |
| Boiling point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) (decomposes) |
| 12.51 g/L | |
| Solubility | Soluble in fuming HCl Insoluble in benzene, diethyl ether and ethanol |
| Vapor pressure | 1·10-9 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.25 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
12,300 mg/kg (rat, oral) 6.000 mg/kg (rat, IV) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Sulfanilamide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sulfanilic acid is an arylsulfonic acid that is mainly used as a precursor for making azo dyes, such as methyl orange, and sulfa drugs, such as sulfanilamide. It is also used in the quantitative analysis of nitrate and nitrite ions. It can be synthesized easily by sulfonation of aniline with concentrated sulfuric acid.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Sulfanilic acid is zwitterionic. It is highly soluble in basic solutions, and moderately soluble in strongly acidic solutions. Its isoelectric point is 1.25, which would be the optimum pH for precipitating and recrystallizing it.[1] It crystallizes from water as a dihydrate, but can be dehydrated by heating.
Physical
Sulfanilic acid is a white solid when pure, but commercial and home made samples are usually off-white or even purple, due to contamination with trace amounts of strongly colored polyaniline compounds.
Availability
Sulfanilic acid may be available from some online chemical suppliers, but is not usually sold to the general public. It is more practical to make if one has access to aniline.
Preparation
The main route for preparation of sulfanilic acid is by sulfonation of aniline using concentrated sulfuric acid.[2]
Projects
- Synthesis of azo dyes:
- Synthesis of sulfanilamide
Handling
Safety
Sulfanilic acid is not particularly dangerous but should be handled with gloves.
Storage
Sulfanilic acid acid is best kept in a clean bottle, away from bases.
Disposal
Neutralize it first using sodium carbonate or bicarbonate, before destroying it with an oxidizing agent.
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19872329
- ↑ http://www.prepchem.com/synthesis-of-sulfanilic-acid/