Difference between revisions of "Alpha-pinene"
(Created page with "257x257px '''α-pinene'''(also written ''alpha''-pinene) is an organic compound with chemical formula C<sub>10</sub>H<sub>16</sub> belonging to...") |
(Fixed grammar and added SMILES code.) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [ | + | {{Chembox |
| − | '''α-pinene'''(also written ''alpha''-pinene) is an organic compound with chemical formula C<sub>10</sub>H<sub>16</sub> belonging to the [[terpenes]], a group of biologically important hydrocarbons. It is the most commonly encountered and well researched of the two pinene isomers, and has a number of niche uses in organic synthesis. | + | | Name = Alpha-pinene |
| + | | Reference = | ||
| + | | IUPACName = (1S,5S)-2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene ((−)-α-Pinene) | ||
| + | | PIN = | ||
| + | | SystematicName = | ||
| + | | OtherNames = α-Pinene<br>Pinene | ||
| + | <!-- Images --> | ||
| + | | ImageFile = Alpha-pinene.png | ||
| + | | ImageSize = 250 | ||
| + | | ImageAlt = | ||
| + | | ImageName = | ||
| + | | ImageFile1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt1 = | ||
| + | | ImageName1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFile2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt2 = | ||
| + | | ImageName2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFile3 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize3 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt3 = | ||
| + | | ImageName3 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR2 = | ||
| + | <!-- Sections --> | ||
| + | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | 3DMet = | ||
| + | | Abbreviations = | ||
| + | | SMILES = CC1=CCC2CC1C2(C)C | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| + | | AtmosphericOHRateConstant = | ||
| + | | Appearance = Colorless liquid | ||
| + | | BoilingPt = | ||
| + | | BoilingPtC = 155 | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | Density = 0.858 g/cm<sup>3</sup> (at 20 °C) | ||
| + | | Formula = C<sub>10</sub>H<sub>16</sub> | ||
| + | | HenryConstant = | ||
| + | | LogP = | ||
| + | | MolarMass = 136.24 g/mol | ||
| + | | MeltingPt = | ||
| + | | MeltingPtC = −64 | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | Odor = Pine, turpentine-like | ||
| + | | pKa = | ||
| + | | pKb = | ||
| + | | Solubility = 0.000249 g/100 ml (25 °C) | ||
| + | | SolubleOther = Miscible with glacial [[acetic acid]], [[acetone]], [[chloroform]], [[diethyl ether]], [[ethanol]], [[isopropanol]]<br>Almost insoluble in [[glycerol]], [[propylene glycol]] | ||
| + | | Solvent = | ||
| + | | VaporPressure = 4.75 mmHg at 25 °C | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | ||
| + | | Coordination = | ||
| + | | CrystalStruct = | ||
| + | | MolShape = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section4 = {{Chembox Thermochemistry | ||
| + | | DeltaGf = | ||
| + | | DeltaHc = | ||
| + | | DeltaHf = | ||
| + | | Entropy = | ||
| + | | HeatCapacity = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section5 = {{Chembox Explosive | ||
| + | | ShockSens = | ||
| + | | FrictionSens = | ||
| + | | DetonationV = | ||
| + | | REFactor = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section6 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| + | | AutoignitionPt = 255 °C (491 °F; 528 K) | ||
| + | | ExploLimits = | ||
| + | | ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/E5qDxMU/alpha-pinene-sa.pdf.html Sigma-Aldrich] | ||
| + | | FlashPt = 33 °C (91 °F; 306 K) | ||
| + | | LD50 = | ||
| + | | LC50 = | ||
| + | | MainHazards = Flammable | ||
| + | | NFPA-F = | ||
| + | | NFPA-H = | ||
| + | | NFPA-R = | ||
| + | | NFPA-S = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section7 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| + | | OtherAnions = | ||
| + | | OtherCations = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction_label = | ||
| + | | OtherCompounds = [[Limonene]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
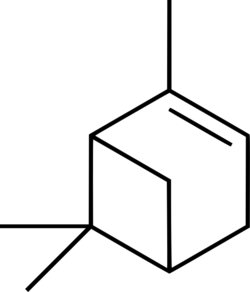
| + | '''α-pinene'''(also written ''alpha''-pinene) is an organic compound with chemical formula '''C<sub>10</sub>H<sub>16</sub>''' belonging to the [[terpenes]], a group of biologically important hydrocarbons. It is the most commonly encountered and well researched of the two pinene isomers, and has a number of niche uses in organic synthesis. | ||
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
===Chemical=== | ===Chemical=== | ||
| + | α-pinene and related compounds are commonly utilized in the fragrance industry, and as such, it is a precursor to many of these compounds. Hydration to [[α-terpineol]] can be accomplished by the reflux of α-pinene with aqueous [[sulfuric acid]] and [[acetone]] for a few hours, or by the action of concentrated sulfuric acid in [[ethanol]]]. The ester α-terpinyl acetate can be produced by esterification with glacial [[acetic acid]]. It can also be rearranged into [[camphene]] by strong acid catalysis in glacial acetic acid as a step in the production of camphor. With dilute acids, terpin hydrate becomes the major product. | ||
| − | + | Addition of [[iodine]] or [[phosphorus trichloride]] causes aromatisation, leading to p-cymene. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Physical=== | ||
α-pinene is a lightweight, clear, colorless liquid in pure form, nearly insoluble in water but miscible with organic solvents. The odor of commercial α-pinene depends on its source; as it can be separated from turpentine by distillation, the odor often matches this. α-pinene boils at 155 °C (311 °F) and is only mildly flammable. | α-pinene is a lightweight, clear, colorless liquid in pure form, nearly insoluble in water but miscible with organic solvents. The odor of commercial α-pinene depends on its source; as it can be separated from turpentine by distillation, the odor often matches this. α-pinene boils at 155 °C (311 °F) and is only mildly flammable. | ||
| + | |||
==Availability== | ==Availability== | ||
| − | α-pinene is readily available as one of the most major | + | α-pinene is readily available as one of the most major constituents of turpentine and can be distilled in reasonably pure form from it. Turpentine is available as a solvent and paint stripper at many hardware and department stores. |
==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 127: | ||
==Projects== | ==Projects== | ||
* Homemade perfumes and fragrances | * Homemade perfumes and fragrances | ||
| − | |||
| + | ==Handling== | ||
===Safety=== | ===Safety=== | ||
While not strongly toxic, α-pinene produces vapors that can cause respiratory problems and may act as a skin irritant as well. It should not be used near open flame due to its flammability. | While not strongly toxic, α-pinene produces vapors that can cause respiratory problems and may act as a skin irritant as well. It should not be used near open flame due to its flammability. | ||
| + | |||
===Storage=== | ===Storage=== | ||
| − | Due to its volatility, α-pinene should be kept in airtight containers away from sources of open | + | Due to its volatility, α-pinene should be kept in airtight containers away from sources of open flames. |
| + | |||
===Disposal=== | ===Disposal=== | ||
| − | α-pinene is commonly encountered in biological systems and does not pose a significant threat to the environment nor to humans. Given its low density and immiscibility with water, pouring it down a sink may not be a good course of action for disposal, with an outdoor trash can presenting a better option. | + | α-pinene is commonly encountered in biological systems and does not pose a significant threat to the environment nor to humans. Given its low density and immiscibility with water, pouring it down a sink may not be a good course of action for disposal, with an outdoor trash can presenting a better option. However, it's best to have it soaked in a porous material, like sand or charcoal, to reduce any leaks on the ground or pavement. |
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
===Relevant Sciencemadness threads=== | ===Relevant Sciencemadness threads=== | ||
| + | *[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=22215 Seperation of Alpha, Beta Pinene from Turpentine] | ||
| + | *[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=64560 α-pinene to α-terpineol acetate] | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Chemical compounds]] | [[Category:Chemical compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Organic compounds]] | [[Category:Organic compounds]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 150: | ||
[[Category:Terpenes]] | [[Category:Terpenes]] | ||
[[Category:Hydrocarbons]] | [[Category:Hydrocarbons]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Liquids]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:53, 25 August 2020
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1S,5S)-2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene ((−)-α-Pinene)
| |
| Other names
α-Pinene
Pinene | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16 | |
| Molar mass | 136.24 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Pine, turpentine-like |
| Density | 0.858 g/cm3 (at 20 °C) |
| Melting point | −64 °C (−83 °F; 209 K) |
| Boiling point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) |
| 0.000249 g/100 ml (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Miscible with glacial acetic acid, acetone, chloroform, diethyl ether, ethanol, isopropanol Almost insoluble in glycerol, propylene glycol |
| Vapor pressure | 4.75 mmHg at 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 33 °C (91 °F; 306 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Limonene |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
α-pinene(also written alpha-pinene) is an organic compound with chemical formula C10H16 belonging to the terpenes, a group of biologically important hydrocarbons. It is the most commonly encountered and well researched of the two pinene isomers, and has a number of niche uses in organic synthesis.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
α-pinene and related compounds are commonly utilized in the fragrance industry, and as such, it is a precursor to many of these compounds. Hydration to α-terpineol can be accomplished by the reflux of α-pinene with aqueous sulfuric acid and acetone for a few hours, or by the action of concentrated sulfuric acid in ethanol]. The ester α-terpinyl acetate can be produced by esterification with glacial acetic acid. It can also be rearranged into camphene by strong acid catalysis in glacial acetic acid as a step in the production of camphor. With dilute acids, terpin hydrate becomes the major product.
Addition of iodine or phosphorus trichloride causes aromatisation, leading to p-cymene.
Physical
α-pinene is a lightweight, clear, colorless liquid in pure form, nearly insoluble in water but miscible with organic solvents. The odor of commercial α-pinene depends on its source; as it can be separated from turpentine by distillation, the odor often matches this. α-pinene boils at 155 °C (311 °F) and is only mildly flammable.
Availability
α-pinene is readily available as one of the most major constituents of turpentine and can be distilled in reasonably pure form from it. Turpentine is available as a solvent and paint stripper at many hardware and department stores.
Preparation
α-pinene is more likely to be extracted from turpentine rather than synthesized in the home lab.
Projects
- Homemade perfumes and fragrances
Handling
Safety
While not strongly toxic, α-pinene produces vapors that can cause respiratory problems and may act as a skin irritant as well. It should not be used near open flame due to its flammability.
Storage
Due to its volatility, α-pinene should be kept in airtight containers away from sources of open flames.
Disposal
α-pinene is commonly encountered in biological systems and does not pose a significant threat to the environment nor to humans. Given its low density and immiscibility with water, pouring it down a sink may not be a good course of action for disposal, with an outdoor trash can presenting a better option. However, it's best to have it soaked in a porous material, like sand or charcoal, to reduce any leaks on the ground or pavement.
References
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
- Chemical pages without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Organic compounds
- Biologically-derived compounds
- Fragrant compounds
- Terpenes
- Hydrocarbons
- Liquids