Difference between revisions of "Methyl salicylate"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Chembox | |
| − | + | | Name = Methyl salicylate | |
| + | | Reference = | ||
| + | | IUPACName = Methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate | ||
| + | | PIN = | ||
| + | | SystematicName = | ||
| + | | OtherNames = Betula oil<br>Gaultheria oil<br>Methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate<br>Oil of wintergreen<br>Salicylic acid methyl ester<br>Wintergreen oil | ||
| + | <!-- Images --> | ||
| + | | ImageFile = | ||
| + | | ImageSize = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt = | ||
| + | | ImageName = | ||
| + | | ImageFile1 = Methyl salicylate.jpg | ||
| + | | ImageSize1 = 300 | ||
| + | | ImageAlt1 = | ||
| + | | ImageName1 = | ||
| + | | ImageCaption1 = Sample of methyl salicylate | ||
| + | | ImageFile2 = Methyl salicylate structure.png | ||
| + | | ImageSize2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt2 = | ||
| + | | ImageName2 = | ||
| + | | ImageCaption2 = The structure of methyl salicylate. | ||
| + | | ImageFile3 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize3 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt3 = | ||
| + | | ImageName3 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR2 = | ||
| + | <!-- Sections --> | ||
| + | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | 3DMet = | ||
| + | | Abbreviations = | ||
| + | | SMILES = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| + | | AtmosphericOHRateConstant = | ||
| + | | Appearance = Colorless viscous liquid | ||
| + | | BoilingPt = | ||
| + | | BoilingPtC = 222 | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | Density = 1.174 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| + | | Formula = C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | | HenryConstant = | ||
| + | | LogP = 2.55 | ||
| + | | MolarMass = 152.15 g/mol | ||
| + | | MeltingPt = | ||
| + | | MeltingPtC = −8.6 | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | pKa = 9.8 | ||
| + | | pKb = | ||
| + | | Solubility = 0.0639 g/100 ml (21 °C)<br>0.0697 g/100 ml (30 °C) | ||
| + | | SolubleOther = Miscible in glacial [[acetic acid]], [[acetone]], [[diethyl ether]], [[ethanol]]br>Soluble in [[chloroform]] | ||
| + | | Solvent = | ||
| + | | VaporPressure = 1 mmHg (54 °C) | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | ||
| + | | Coordination = | ||
| + | | CrystalStruct = | ||
| + | | MolShape = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section4 = {{Chembox Thermochemistry | ||
| + | | DeltaGf = | ||
| + | | DeltaHc = | ||
| + | | DeltaHf = | ||
| + | | Entropy = | ||
| + | | HeatCapacity = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section5 = {{Chembox Explosive | ||
| + | | ShockSens = | ||
| + | | FrictionSens = | ||
| + | | DetonationV = | ||
| + | | REFactor = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section6 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| + | | AutoignitionPt = 452.7 °C (846.9 °F; 725.8 K) | ||
| + | | ExploLimits = | ||
| + | | ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/GskgPpo/methyl-salicylate-sa.pdf.html Sigma-Aldrich] | ||
| + | | FlashPt = 96 °C (205 °F; 369 K) | ||
| + | | LD50 = | ||
| + | | LC50 = | ||
| + | | MainHazards = Irritant | ||
| + | | NFPA-F = | ||
| + | | NFPA-H = | ||
| + | | NFPA-R = | ||
| + | | NFPA-S = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section7 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| + | | OtherAnions = | ||
| + | | OtherCations = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction_label = | ||
| + | | OtherCompounds = [[Salicylic acid]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
'''Methyl salicylate''' is an organic [[ester]] known widely for its easy synthesis and pleasing aroma. It is often referred to as oil of wintergreen, the plant from which it was historically produced, and occurs in many different foods and drinks. | '''Methyl salicylate''' is an organic [[ester]] known widely for its easy synthesis and pleasing aroma. It is often referred to as oil of wintergreen, the plant from which it was historically produced, and occurs in many different foods and drinks. | ||
Revision as of 11:19, 5 June 2017
 Sample of methyl salicylate
| |
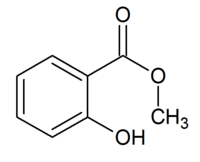 The structure of methyl salicylate.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate
| |
| Other names
Betula oil
Gaultheria oil Methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate Oil of wintergreen Salicylic acid methyl ester Wintergreen oil | |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.15 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless viscous liquid |
| Density | 1.174 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −8.6 °C (16.5 °F; 264.5 K) |
| Boiling point | 222 °C (432 °F; 495 K) |
| 0.0639 g/100 ml (21 °C) 0.0697 g/100 ml (30 °C) | |
| Solubility | Miscible in glacial acetic acid, acetone, diethyl ether, ethanolbr>Soluble in chloroform |
| Vapor pressure | 1 mmHg (54 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.8 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 96 °C (205 °F; 369 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Salicylic acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Methyl salicylate is an organic ester known widely for its easy synthesis and pleasing aroma. It is often referred to as oil of wintergreen, the plant from which it was historically produced, and occurs in many different foods and drinks.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Methyl salicylate is typically produced for its characteristic odor rather than as a reagent. Though used often as a flavorant and fragrance, these make use of methyl salicylate at a very low concentration, as it is quite toxic. It also finds limited use as an antiseptic.
Physical
Methyl salicylate typically exists as a transparent light oil with very limited water solubility that can be frozen at temperatures below −8.6 °C (16.5 °F). Homemade samples may have a yellow, green, or violet coloration depending on the impurities present in the reactants. The most striking characteristic of methyl salicylate is its potent "minty" aroma that can best be described as that found in wintergreen scented and flavored products. It may also be recognized as one of the chief flavoring and smell components of modern root beer.
Methyl salicylate exhibits blue fluorescence. Wint-O-Green LifeSavers are visibly triboluminescent due to their methyl salicylate and sucrose (which emits UV light when crushed) content.
Availability
Oil of wintergreen may be purchasable at some pharmacies and fragrance stores. It is a very common component in scented oils and flavorings but at a low concentration. Isopropanol may be bought with dissolved methyl salicylate in certain localities. It is often dyed green.
Preparation
Methyl salicylate is produced by the esterification of methanol and salicylic acid in the presence of a dehydrating agent, typically sulfuric acid, at temperatures close to the boiling point of methanol. This is best accomplished under a reflux setup, which consists of continual vaporization and condensation in a closed system for up to several hours depending on the amount being produced. Because esterifications such as this readily proceed in either direction between reactants and products, a good yield is difficult to obtain simply by carrying out this procedure. Some ways to drive the reaction further towards the right include using a large excess of methanol, increasing the amount of sulfuric acid, and most importantly, removing water from the reaction mixture by some means. This could mean the addition of a desiccant such as anhydrous calcium sulfate. The sulfuric acid in the reaction mixture can be removed using calcium carbonate, which reacts to produce more calcium sulfate, which is easily filtered out.
Projects
- Make an air freshener
Handling
Safety
Oil of wintergreen is fairly toxic in a way similar to aspirin, due to both chemicals being metabolized similarly in the body. Methyl salicylate is essentially harmless in practice unless it is intentionally consumed at high concentrations. Edible substances containing wintergreen typically contain less than one percent, making it difficult for them to be sufficiently toxic.
Storage
Methyl salicylate should be stored in closed bottles.
Disposal
Methyl salicylate can be safely burned, either alone or mixed with a more flammable and volatile solvent, like ethanol. Since it breaks down into salicylic acid and methanol, small amounts can be poured down the drain.