Difference between revisions of "Methyl formate"
(Added image) |
|||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
[[Category:Fragrant compounds]] | [[Category:Fragrant compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Volatile chemicals]] | [[Category:Volatile chemicals]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Materials unstable in basic solution]] | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 3 March 2016
 |
This article is a stub. Please help Sciencemadness Wiki by expanding it, adding pictures, and improving existing text.
|
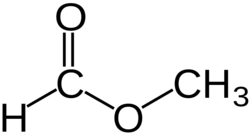
Methyl formate or methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid, the simplest ester.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Methyl formate can be hydrolyzed to methanol and formic acid.
Physical
Methyl formate is a colorless organic liquid, with an ethereal odor, low surface tension and high vapor pressure. Its melting point is at −100 °C and boils at 32 °C. It has a density of 0.97 g/cm3. It is soluble in water (30g/100 ml) and other solvents, such as ethyl ether, acetone. Its flash point is -19°C and its auto-ignition temperature is 449°C.
Availability
Methyl formate is available from chemical suppliers.
Preparation
Methyl formate can be synthesized by reacting anhydrous formic acid with dry methanol, over a strong desiccant, such as calcium chloride.
Industrially, it is prepared by via carbonylation of methanol, using sodium methoxide as a catalyst and pyridine as a temperature promoter, in an extremely dry medium. The smallest traces of water can disrupt the reaction.
- CH3OH + CO → HCOOCH3[1]
Projects
- Formamide synthesis
- Organic extractions
Handling
Safety
Methyl formate vapors may irritate lungs, so it's best to work in a well ventilated area. Since its boiling point is lower than the human body temperature, samples of methyl formate should not be kept too long in hand.
Storage
Due to its low boiling point, Methyl formate should be stored in closed bottles, away from any source of heat or light, preferable in a fridge. This is mandatory during hot summers.
Disposal
Methyl formate can be safely burned.